#include "rcl/allocator.h"#include "rcl/macros.h"#include "rcl/types.h"#include "rcl/visibility_control.h"#include "rcutils/time.h"
Go to the source code of this file.
Classes | |
| struct | rcl_duration_s |
| A duration of time, measured in nanoseconds and its source. More... | |
| struct | rcl_time_jump_s |
| Struct to describe a jump in time. More... | |
| struct | rcl_jump_threshold_s |
| Describe the prerequisites for calling a time jump callback. More... | |
| struct | rcl_jump_callback_info_s |
| Struct to describe an added callback. More... | |
| struct | rcl_clock_s |
| Encapsulation of a time source. More... | |
| struct | rcl_time_point_s |
| A single point in time, measured in nanoseconds, the reference point is based on the source. More... | |
Macros | |
| #define | RCL_S_TO_NS RCUTILS_S_TO_NS |
| Convenience macro to convert seconds to nanoseconds. | |
| #define | RCL_MS_TO_NS RCUTILS_MS_TO_NS |
| Convenience macro to convert milliseconds to nanoseconds. | |
| #define | RCL_US_TO_NS RCUTILS_US_TO_NS |
| Convenience macro to convert microseconds to nanoseconds. | |
| #define | RCL_NS_TO_S RCUTILS_NS_TO_S |
| Convenience macro to convert nanoseconds to seconds. | |
| #define | RCL_NS_TO_MS RCUTILS_NS_TO_MS |
| Convenience macro to convert nanoseconds to milliseconds. | |
| #define | RCL_NS_TO_US RCUTILS_NS_TO_US |
| Convenience macro to convert nanoseconds to microseconds. | |
Typedefs | |
| typedef rcutils_time_point_value_t | rcl_time_point_value_t |
| A single point in time, measured in nanoseconds since the Unix epoch. | |
| typedef rcutils_duration_value_t | rcl_duration_value_t |
| A duration of time, measured in nanoseconds. | |
| typedef enum rcl_clock_type_e | rcl_clock_type_t |
| Time source type, used to indicate the source of a time measurement. More... | |
| typedef struct rcl_duration_s | rcl_duration_t |
| A duration of time, measured in nanoseconds and its source. | |
| typedef enum rcl_clock_change_e | rcl_clock_change_t |
| Enumeration to describe the type of time jump. | |
| typedef struct rcl_time_jump_s | rcl_time_jump_t |
| Struct to describe a jump in time. | |
| typedef void(* | rcl_jump_callback_t) (const rcl_time_jump_t *time_jump, bool before_jump, void *user_data) |
| typedef struct rcl_jump_threshold_s | rcl_jump_threshold_t |
| Describe the prerequisites for calling a time jump callback. | |
| typedef struct rcl_jump_callback_info_s | rcl_jump_callback_info_t |
| Struct to describe an added callback. | |
| typedef struct rcl_clock_s | rcl_clock_t |
| Encapsulation of a time source. | |
| typedef struct rcl_time_point_s | rcl_time_point_t |
| A single point in time, measured in nanoseconds, the reference point is based on the source. | |
Enumerations | |
| enum | rcl_clock_type_e { RCL_CLOCK_UNINITIALIZED = 0 , RCL_ROS_TIME , RCL_SYSTEM_TIME , RCL_STEADY_TIME } |
| Time source type, used to indicate the source of a time measurement. More... | |
| enum | rcl_clock_change_e { RCL_ROS_TIME_NO_CHANGE = 1 , RCL_ROS_TIME_ACTIVATED = 2 , RCL_ROS_TIME_DEACTIVATED = 3 , RCL_SYSTEM_TIME_NO_CHANGE = 4 } |
| Enumeration to describe the type of time jump. More... | |
Functions | |
| RCL_PUBLIC RCL_WARN_UNUSED bool | rcl_clock_time_started (rcl_clock_t *clock) |
| Check if the clock has started. More... | |
| RCL_PUBLIC RCL_WARN_UNUSED bool | rcl_clock_valid (rcl_clock_t *clock) |
| Check if the clock has valid values. More... | |
| RCL_PUBLIC RCL_WARN_UNUSED rcl_ret_t | rcl_clock_init (rcl_clock_type_t clock_type, rcl_clock_t *clock, rcl_allocator_t *allocator) |
| Initialize a clock based on the passed type. More... | |
| RCL_PUBLIC RCL_WARN_UNUSED rcl_ret_t | rcl_clock_fini (rcl_clock_t *clock) |
| Finalize a clock. More... | |
| RCL_PUBLIC RCL_WARN_UNUSED rcl_ret_t | rcl_ros_clock_init (rcl_clock_t *clock, rcl_allocator_t *allocator) |
| Initialize a clock as a RCL_ROS_TIME time source. More... | |
| RCL_PUBLIC RCL_WARN_UNUSED rcl_ret_t | rcl_ros_clock_fini (rcl_clock_t *clock) |
| Finalize a clock as a RCL_ROS_TIME time source. More... | |
| RCL_PUBLIC RCL_WARN_UNUSED rcl_ret_t | rcl_steady_clock_init (rcl_clock_t *clock, rcl_allocator_t *allocator) |
| Initialize a clock as a RCL_STEADY_TIME time source. More... | |
| RCL_PUBLIC RCL_WARN_UNUSED rcl_ret_t | rcl_steady_clock_fini (rcl_clock_t *clock) |
| Finalize a clock as a RCL_STEADY_TIME time source. More... | |
| RCL_PUBLIC RCL_WARN_UNUSED rcl_ret_t | rcl_system_clock_init (rcl_clock_t *clock, rcl_allocator_t *allocator) |
| Initialize a clock as a RCL_SYSTEM_TIME time source. More... | |
| RCL_PUBLIC RCL_WARN_UNUSED rcl_ret_t | rcl_system_clock_fini (rcl_clock_t *clock) |
| Finalize a clock as a RCL_SYSTEM_TIME time source. More... | |
| RCL_PUBLIC RCL_WARN_UNUSED rcl_ret_t | rcl_difference_times (const rcl_time_point_t *start, const rcl_time_point_t *finish, rcl_duration_t *delta) |
| Compute the difference between two time points. More... | |
| RCL_PUBLIC RCL_WARN_UNUSED rcl_ret_t | rcl_clock_get_now (rcl_clock_t *clock, rcl_time_point_value_t *time_point_value) |
| Fill the time point value with the current value of the associated clock. More... | |
| RCL_PUBLIC RCL_WARN_UNUSED rcl_ret_t | rcl_enable_ros_time_override (rcl_clock_t *clock) |
| Enable the ROS time abstraction override. More... | |
| RCL_PUBLIC RCL_WARN_UNUSED rcl_ret_t | rcl_disable_ros_time_override (rcl_clock_t *clock) |
| Disable the ROS time abstraction override. More... | |
| RCL_PUBLIC RCL_WARN_UNUSED rcl_ret_t | rcl_is_enabled_ros_time_override (rcl_clock_t *clock, bool *is_enabled) |
| Check if the RCL_ROS_TIME time source has the override enabled. More... | |
| RCL_PUBLIC RCL_WARN_UNUSED rcl_ret_t | rcl_set_ros_time_override (rcl_clock_t *clock, rcl_time_point_value_t time_value) |
| Set the current time for this RCL_ROS_TIME time source. More... | |
| RCL_PUBLIC RCL_WARN_UNUSED rcl_ret_t | rcl_clock_add_jump_callback (rcl_clock_t *clock, rcl_jump_threshold_t threshold, rcl_jump_callback_t callback, void *user_data) |
| Add a callback to be called when a time jump exceeds a threshold. More... | |
| RCL_PUBLIC RCL_WARN_UNUSED rcl_ret_t | rcl_clock_remove_jump_callback (rcl_clock_t *clock, rcl_jump_callback_t callback, void *user_data) |
| Remove a previously added time jump callback. More... | |
Typedef Documentation
◆ rcl_clock_type_t
| typedef enum rcl_clock_type_e rcl_clock_type_t |
Time source type, used to indicate the source of a time measurement.
RCL_ROS_TIME will report the latest value reported by a ROS time source, or if a ROS time source is not active it reports the same as RCL_SYSTEM_TIME. For more information about ROS time sources, refer to the design document: http://design.ros2.org/articles/clock_and_time.html
RCL_SYSTEM_TIME reports the same value as the system clock.
RCL_STEADY_TIME reports a value from a monotonically increasing clock.
◆ rcl_jump_callback_t
| typedef void(* rcl_jump_callback_t) (const rcl_time_jump_t *time_jump, bool before_jump, void *user_data) |
Signature of a time jump callback.
- Parameters
-
[in] time_jump A description of the jump in time. [in] before_jump Every jump callback is called twice: once before the clock changes and once after. This is true the first call and false the second. [in] user_data A pointer given at callback registration which is passed to the callback.
Enumeration Type Documentation
◆ rcl_clock_change_e
| enum rcl_clock_change_e |
Enumeration to describe the type of time jump.
◆ rcl_clock_type_e
| enum rcl_clock_type_e |
Time source type, used to indicate the source of a time measurement.
RCL_ROS_TIME will report the latest value reported by a ROS time source, or if a ROS time source is not active it reports the same as RCL_SYSTEM_TIME. For more information about ROS time sources, refer to the design document: http://design.ros2.org/articles/clock_and_time.html
RCL_SYSTEM_TIME reports the same value as the system clock.
RCL_STEADY_TIME reports a value from a monotonically increasing clock.
| Enumerator | |
|---|---|
| RCL_CLOCK_UNINITIALIZED | Clock uninitialized. |
| RCL_ROS_TIME | Use ROS time. |
| RCL_SYSTEM_TIME | Use system time. |
| RCL_STEADY_TIME | Use a steady clock time. |
Function Documentation
◆ rcl_clock_add_jump_callback()
| RCL_PUBLIC RCL_WARN_UNUSED rcl_ret_t rcl_clock_add_jump_callback | ( | rcl_clock_t * | clock, |
| rcl_jump_threshold_t | threshold, | ||
| rcl_jump_callback_t | callback, | ||
| void * | user_data | ||
| ) |
Add a callback to be called when a time jump exceeds a threshold.
The callback is called twice when the threshold is exceeded: once before the clock is updated, and once after. The user_data pointer is passed to the callback as the last argument. A callback and user_data pair must be unique among the callbacks added to a clock.
This function is not thread-safe with rcl_clock_remove_jump_callback(), rcl_enable_ros_time_override(), rcl_disable_ros_time_override() nor rcl_set_ros_time_override() functions when used on the same clock object.
| Attribute | Adherence |
|---|---|
| Allocates Memory | Yes |
| Thread-Safe | No [1] |
| Uses Atomics | No |
| Lock-Free | Yes |
[1] Function is reentrant, but concurrent calls on the same clock object are not safe. Thread-safety is also affected by that of the allocator object associated with the clock object.
- Parameters
-
[in] clock A clock to add a jump callback to. [in] threshold Criteria indicating when to call the callback. [in] callback A callback to call. [in] user_data A pointer to be passed to the callback.
- Returns
- RCL_RET_OK if the callback was added successfully, or
- RCL_RET_BAD_ALLOC if a memory allocation failed, or
- RCL_RET_INVALID_ARGUMENT if any arguments are invalid, or
- RCL_RET_ERROR an unspecified error occurs.
Definition at line 392 of file time.c.
References rcl_clock_s::allocator, rcl_jump_callback_info_s::callback, rcl_clock_s::jump_callbacks, rcl_jump_threshold_s::min_backward, rcl_jump_threshold_s::min_forward, rcl_duration_s::nanoseconds, rcl_clock_s::num_jump_callbacks, RCL_CHECK_ALLOCATOR_WITH_MSG, RCL_RET_BAD_ALLOC, RCL_RET_ERROR, RCL_RET_INVALID_ARGUMENT, RCL_RET_OK, rcl_jump_callback_info_s::threshold, and rcl_jump_callback_info_s::user_data.
Referenced by rclcpp::Clock::create_jump_callback(), and rcl_timer_init2().
◆ rcl_clock_fini()
| RCL_PUBLIC RCL_WARN_UNUSED rcl_ret_t rcl_clock_fini | ( | rcl_clock_t * | clock | ) |
Finalize a clock.
This will deallocate all necessary internal structures, and clean up any variables. It can be combined with any of the init functions.
Passing a clock with type RCL_CLOCK_UNINITIALIZED will result in RCL_RET_INVALID_ARGUMENT being returned.
This function is not thread-safe with any other function operating on the same clock object.
| Attribute | Adherence |
|---|---|
| Allocates Memory | No |
| Thread-Safe | No [1] |
| Uses Atomics | No |
| Lock-Free | Yes |
[1] Function is reentrant, but concurrent calls on the same clock object are not safe. Thread-safety is also affected by that of the allocator object associated with the clock object.
- Parameters
-
[in] clock the handle to the clock which is being finalized
- Returns
- RCL_RET_OK if the time source was successfully finalized, or
- RCL_RET_INVALID_ARGUMENT if any arguments are invalid, or
- RCL_RET_ERROR an unspecified error occur.
Definition at line 132 of file time.c.
References rcl_clock_s::allocator, RCL_CHECK_ALLOCATOR_WITH_MSG, RCL_CLOCK_UNINITIALIZED, RCL_RET_ERROR, RCL_RET_INVALID_ARGUMENT, rcl_ros_clock_fini(), RCL_ROS_TIME, rcl_steady_clock_fini(), RCL_STEADY_TIME, rcl_system_clock_fini(), RCL_SYSTEM_TIME, and rcl_clock_s::type.
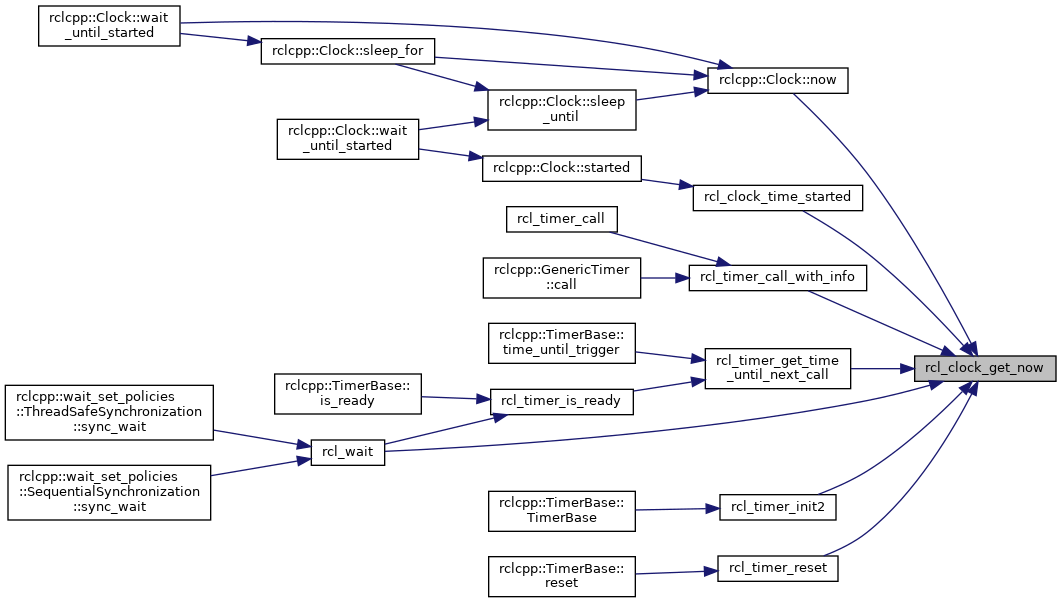
◆ rcl_clock_get_now()
| RCL_PUBLIC RCL_WARN_UNUSED rcl_ret_t rcl_clock_get_now | ( | rcl_clock_t * | clock, |
| rcl_time_point_value_t * | time_point_value | ||
| ) |
Fill the time point value with the current value of the associated clock.
This function will populate the data of the time_point_value object with the current value from it's associated time abstraction.
| Attribute | Adherence |
|---|---|
| Allocates Memory | No |
| Thread-Safe | Yes |
| Uses Atomics | Yes [1] |
| Lock-Free | Yes |
[1] If clock is of RCL_ROS_TIME type.
- Parameters
-
[in] clock The time source from which to set the value. [out] time_point_value The time_point value to populate.
- Returns
- RCL_RET_OK if the last call time was retrieved successfully, or
- RCL_RET_INVALID_ARGUMENT if any arguments are invalid, or
- RCL_RET_ERROR an unspecified error occur.
Definition at line 263 of file time.c.
References rcl_clock_s::data, rcl_clock_s::get_now, RCL_RET_ERROR, RCL_RET_INVALID_ARGUMENT, and rcl_clock_s::type.
Referenced by rclcpp::Clock::now(), rcl_clock_time_started(), rcl_timer_call_with_info(), rcl_timer_get_time_until_next_call(), rcl_timer_init2(), rcl_timer_reset(), and rcl_wait().
◆ rcl_clock_init()
| RCL_PUBLIC RCL_WARN_UNUSED rcl_ret_t rcl_clock_init | ( | rcl_clock_type_t | clock_type, |
| rcl_clock_t * | clock, | ||
| rcl_allocator_t * | allocator | ||
| ) |
Initialize a clock based on the passed type.
This will allocate all necessary internal structures, and initialize variables.
| Attribute | Adherence |
|---|---|
| Allocates Memory | Yes [1] |
| Thread-Safe | No [2] |
| Uses Atomics | No |
| Lock-Free | Yes |
[1] If clock_type is RCL_ROS_TIME [2] Function is reentrant, but concurrent calls on the same clock object are not safe. Thread-safety is also affected by that of the allocator object.
- Parameters
-
[in] clock_type the type identifying the time source to provide [in] clock the handle to the clock which is being initialized [in] allocator The allocator to use for allocations
- Returns
- RCL_RET_OK if the time source was successfully initialized, or
- RCL_RET_INVALID_ARGUMENT if any arguments are invalid, or
- RCL_RET_ERROR an unspecified error occur.
Definition at line 98 of file time.c.
References RCL_CHECK_ALLOCATOR_WITH_MSG, RCL_CLOCK_UNINITIALIZED, RCL_RET_INVALID_ARGUMENT, RCL_RET_OK, rcl_ros_clock_init(), RCL_ROS_TIME, rcl_steady_clock_init(), RCL_STEADY_TIME, rcl_system_clock_init(), and RCL_SYSTEM_TIME.
◆ rcl_clock_remove_jump_callback()
| RCL_PUBLIC RCL_WARN_UNUSED rcl_ret_t rcl_clock_remove_jump_callback | ( | rcl_clock_t * | clock, |
| rcl_jump_callback_t | callback, | ||
| void * | user_data | ||
| ) |
Remove a previously added time jump callback.
This function is not thread-safe with rcl_clock_add_jump_callback() rcl_enable_ros_time_override(), rcl_disable_ros_time_override() nor rcl_set_ros_time_override() functions when used on the same clock object.
| Attribute | Adherence |
|---|---|
| Allocates Memory | Yes |
| Thread-Safe | No [1] |
| Uses Atomics | No |
| Lock-Free | Yes |
[1] Function is reentrant, but concurrent calls on the same clock object are not safe. Thread-safety is also affected by that of the allocator object associated with the clock object.
- Parameters
-
[in] clock The clock to remove a jump callback from. [in] callback The callback to call. [in] user_data A pointer to be passed to the callback.
- Returns
- RCL_RET_OK if the callback was added successfully, or
- RCL_RET_BAD_ALLOC if a memory allocation failed, or
- RCL_RET_INVALID_ARGUMENT if any arguments are invalid, or
- RCL_RET_ERROR the callback was not found or an unspecified error occurs.
Definition at line 436 of file time.c.
References rcl_clock_s::allocator, rcl_jump_callback_info_s::callback, rcl_clock_s::jump_callbacks, rcl_clock_s::num_jump_callbacks, RCL_CHECK_ALLOCATOR_WITH_MSG, RCL_RET_BAD_ALLOC, RCL_RET_ERROR, RCL_RET_INVALID_ARGUMENT, RCL_RET_OK, and rcl_jump_callback_info_s::user_data.
Referenced by rcl_timer_fini(), and rcl_timer_init2().
◆ rcl_clock_time_started()
| RCL_PUBLIC RCL_WARN_UNUSED bool rcl_clock_time_started | ( | rcl_clock_t * | clock | ) |
Check if the clock has started.
This function returns true if the clock contains a time point value that is non-zero. Note that if data is uninitialized it may give a false positive.
This function is primarily used to check if a clock using ROS time has started. This is because it is possible that a simulator might be initialized paused, causing ROS time to be 0 until it is unpaused.
| Attribute | Adherence |
|---|---|
| Allocates Memory | No |
| Thread-Safe | Yes |
| Uses Atomics | No |
| Lock-Free | Yes |
- Parameters
-
[in] clock the handle to the clock which is being queried
- Returns
- true if the clock has started, otherwise return false.
Definition at line 76 of file time.c.
References rcl_clock_get_now(), and RCL_RET_OK.
Referenced by rclcpp::Clock::started().

◆ rcl_clock_valid()
| RCL_PUBLIC RCL_WARN_UNUSED bool rcl_clock_valid | ( | rcl_clock_t * | clock | ) |
Check if the clock has valid values.
This function returns true if the time source appears to be valid. It will check that the type is not uninitialized, and that pointers are not invalid. Note that if data is uninitialized it may give a false positive.
| Attribute | Adherence |
|---|---|
| Allocates Memory | No |
| Thread-Safe | Yes |
| Uses Atomics | No |
| Lock-Free | Yes |
- Parameters
-
[in] clock the handle to the clock which is being queried
- Returns
- true if the source is believed to be valid, otherwise return false.
Definition at line 86 of file time.c.
References rcl_clock_s::get_now, RCL_CLOCK_UNINITIALIZED, and rcl_clock_s::type.
Referenced by rclcpp::Clock::ros_time_is_active(), rclcpp::Clock::started(), and rclcpp::Clock::wait_until_started().
◆ rcl_difference_times()
| RCL_PUBLIC RCL_WARN_UNUSED rcl_ret_t rcl_difference_times | ( | const rcl_time_point_t * | start, |
| const rcl_time_point_t * | finish, | ||
| rcl_duration_t * | delta | ||
| ) |
Compute the difference between two time points.
This function takes two time points and computes the duration between them. The two time points must be using the same time abstraction, and the resultant duration will also be of the same abstraction.
The value will be computed as duration = finish - start. If start is after finish the duration will be negative.
| Attribute | Adherence |
|---|---|
| Allocates Memory | No |
| Thread-Safe | Yes |
| Uses Atomics | No |
| Lock-Free | Yes |
- Parameters
-
[in] start The time point for the start of the duration. [in] finish The time point for the end of the duration. [out] delta The duration between the start and finish.
- Returns
- RCL_RET_OK if the difference was computed successfully, or
- RCL_RET_INVALID_ARGUMENT if any arguments are invalid, or
- RCL_RET_ERROR an unspecified error occur.
Definition at line 243 of file time.c.
References rcl_time_point_s::clock_type, rcl_duration_s::nanoseconds, rcl_time_point_s::nanoseconds, RCL_RET_ERROR, RCL_RET_INVALID_ARGUMENT, and RCL_RET_OK.
◆ rcl_disable_ros_time_override()
| RCL_PUBLIC RCL_WARN_UNUSED rcl_ret_t rcl_disable_ros_time_override | ( | rcl_clock_t * | clock | ) |
Disable the ROS time abstraction override.
This method will disable the RCL_ROS_TIME time abstraction override values, such that the time source will report the system time even if a custom value has been set.
This function is not thread-safe with rcl_clock_add_jump_callback(), nor rcl_clock_remove_jump_callback() functions when used on the same clock object.
| Attribute | Adherence [1] |
|---|---|
| Allocates Memory | No |
| Thread-Safe | No [2] |
| Uses Atomics | No |
| Lock-Free | Yes |
[1] Only applies to the function itself, as jump callbacks may not abide to it. [2] Function is reentrant, but concurrent calls on the same clock object are not safe.
- Parameters
-
[in] clock The clock to disable.
- Returns
- RCL_RET_OK if the time source was disabled successfully, or
- RCL_RET_INVALID_ARGUMENT if any arguments are invalid, or
- RCL_RET_ERROR an unspecified error occur.
Definition at line 321 of file time.c.
References rcl_time_jump_s::clock_change, rcl_clock_s::data, rcl_time_jump_s::delta, rcl_duration_s::nanoseconds, RCL_RET_ERROR, RCL_RET_INVALID_ARGUMENT, RCL_RET_OK, RCL_ROS_TIME, RCL_ROS_TIME_DEACTIVATED, and rcl_clock_s::type.
◆ rcl_enable_ros_time_override()
| RCL_PUBLIC RCL_WARN_UNUSED rcl_ret_t rcl_enable_ros_time_override | ( | rcl_clock_t * | clock | ) |
Enable the ROS time abstraction override.
This method will enable the ROS time abstraction override values, such that the time source will report the set value instead of falling back to system time.
This function is not thread-safe with rcl_clock_add_jump_callback(), nor rcl_clock_remove_jump_callback() functions when used on the same clock object.
| Attribute | Adherence [1] |
|---|---|
| Allocates Memory | No |
| Thread-Safe | No [2] |
| Uses Atomics | No |
| Lock-Free | Yes |
[1] Only applies to the function itself, as jump callbacks may not abide to it. [2] Function is reentrant, but concurrent calls on the same clock object are not safe.
- Parameters
-
[in] clock The clock to enable.
- Returns
- RCL_RET_OK if the time source was enabled successfully, or
- RCL_RET_INVALID_ARGUMENT if any arguments are invalid, or
- RCL_RET_ERROR an unspecified error occur.
Definition at line 299 of file time.c.
References rcl_time_jump_s::clock_change, rcl_clock_s::data, rcl_time_jump_s::delta, rcl_duration_s::nanoseconds, RCL_RET_ERROR, RCL_RET_INVALID_ARGUMENT, RCL_RET_OK, RCL_ROS_TIME, RCL_ROS_TIME_ACTIVATED, and rcl_clock_s::type.
◆ rcl_is_enabled_ros_time_override()
| RCL_PUBLIC RCL_WARN_UNUSED rcl_ret_t rcl_is_enabled_ros_time_override | ( | rcl_clock_t * | clock, |
| bool * | is_enabled | ||
| ) |
Check if the RCL_ROS_TIME time source has the override enabled.
This will populate the is_enabled object to indicate if the time overide is enabled. If it is enabled, the set value will be returned. Otherwise this time source will return the equivalent to system time abstraction.
This function is not thread-safe with rcl_enable_ros_time_override() nor rcl_disable_ros_time_override() functions when used on the same clock object.
| Attribute | Adherence |
|---|---|
| Allocates Memory | No |
| Thread-Safe | No [1] |
| Uses Atomics | No |
| Lock-Free | Yes |
[1] Function is reentrant, but concurrent calls on the same clock object are not safe.
- Parameters
-
[in] clock The clock to query. [out] is_enabled Whether the override is enabled..
- Returns
- RCL_RET_OK if the time source was queried successfully, or
- RCL_RET_INVALID_ARGUMENT if any arguments are invalid, or
- RCL_RET_ERROR an unspecified error occur.
Definition at line 343 of file time.c.
References rcl_clock_s::data, RCL_RET_ERROR, RCL_RET_INVALID_ARGUMENT, RCL_RET_OK, RCL_ROS_TIME, and rcl_clock_s::type.
Referenced by rcl_wait(), and rclcpp::Clock::ros_time_is_active().
◆ rcl_ros_clock_fini()
| RCL_PUBLIC RCL_WARN_UNUSED rcl_ret_t rcl_ros_clock_fini | ( | rcl_clock_t * | clock | ) |
Finalize a clock as a RCL_ROS_TIME time source.
This will deallocate all necessary internal structures, and clean up any variables. It is specifically setting up a RCL_ROS_TIME time source. It is expected to be paired with the init fuction.
This function is not thread-safe with any other function operating on the same clock object.
| Attribute | Adherence |
|---|---|
| Allocates Memory | No |
| Thread-Safe | No [1] |
| Uses Atomics | No |
| Lock-Free | Yes |
[1] Function is reentrant, but concurrent calls on the same clock object are not safe. Thread-safety is also affected by that of the allocator object associated with the clock object.
- Parameters
-
[in] clock the handle to the clock which is being initialized
- Returns
- RCL_RET_OK if the time source was successfully finalized, or
- RCL_RET_INVALID_ARGUMENT if any arguments are invalid, or
- RCL_RET_ERROR an unspecified error occur.
Definition at line 176 of file time.c.
References rcl_clock_s::allocator, rcl_clock_s::data, RCL_RET_ERROR, RCL_RET_INVALID_ARGUMENT, RCL_RET_OK, RCL_ROS_TIME, and rcl_clock_s::type.
Referenced by rcl_clock_fini().
◆ rcl_ros_clock_init()
| RCL_PUBLIC RCL_WARN_UNUSED rcl_ret_t rcl_ros_clock_init | ( | rcl_clock_t * | clock, |
| rcl_allocator_t * | allocator | ||
| ) |
Initialize a clock as a RCL_ROS_TIME time source.
This will allocate all necessary internal structures, and initialize variables. It is specifically setting up a RCL_ROS_TIME time source.
| Attribute | Adherence |
|---|---|
| Allocates Memory | Yes |
| Thread-Safe | No [1] |
| Uses Atomics | No |
| Lock-Free | Yes |
[2] Function is reentrant, but concurrent calls on the same clock object are not safe. Thread-safety is also affected by that of the allocator object.
- Parameters
-
[in] clock the handle to the clock which is being initialized [in] allocator The allocator to use for allocations
- Returns
- RCL_RET_OK if the time source was successfully initialized, or
- RCL_RET_INVALID_ARGUMENT if any arguments are invalid, or
- RCL_RET_BAD_ALLOC if allocating memory failed, or
- RCL_RET_ERROR an unspecified error occur.
Definition at line 153 of file time.c.
References rcl_clock_s::data, rcl_clock_s::get_now, RCL_RET_BAD_ALLOC, RCL_RET_INVALID_ARGUMENT, RCL_RET_OK, RCL_ROS_TIME, and rcl_clock_s::type.
Referenced by rcl_clock_init().
◆ rcl_set_ros_time_override()
| RCL_PUBLIC RCL_WARN_UNUSED rcl_ret_t rcl_set_ros_time_override | ( | rcl_clock_t * | clock, |
| rcl_time_point_value_t | time_value | ||
| ) |
Set the current time for this RCL_ROS_TIME time source.
This function will update the internal storage for the RCL_ROS_TIME time source. If queried and override enabled the time source will return this value, otherwise it will return the system time.
This function is not thread-safe with rcl_clock_add_jump_callback(), nor rcl_clock_remove_jump_callback() functions when used on the same clock object.
| Attribute | Adherence [1] |
|---|---|
| Allocates Memory | No |
| Thread-Safe | No [2] |
| Uses Atomics | Yes |
| Lock-Free | Yes |
[1] Only applies to the function itself, as jump callbacks may not abide to it. [2] Function is reentrant, but concurrent calls on the same clock object are not safe.
- Parameters
-
[in] clock The clock to update. [in] time_value The new current time.
- Returns
- RCL_RET_OK if the time source was set successfully, or
- RCL_RET_INVALID_ARGUMENT if any arguments are invalid, or
- RCL_RET_ERROR an unspecified error occur.
Definition at line 361 of file time.c.
References rcl_time_jump_s::clock_change, rcl_clock_s::data, rcl_time_jump_s::delta, rcl_duration_s::nanoseconds, RCL_RET_ERROR, RCL_RET_INVALID_ARGUMENT, RCL_RET_OK, RCL_ROS_TIME, RCL_ROS_TIME_NO_CHANGE, and rcl_clock_s::type.
◆ rcl_steady_clock_fini()
| RCL_PUBLIC RCL_WARN_UNUSED rcl_ret_t rcl_steady_clock_fini | ( | rcl_clock_t * | clock | ) |
Finalize a clock as a RCL_STEADY_TIME time source.
Finalize the clock as a RCL_STEADY_TIME time source.
This will deallocate all necessary internal structures, and clean up any variables. It is specifically setting up a steady time source. It is expected to be paired with the init fuction.
This function is not thread-safe with any other function operating on the same clock object.
| Attribute | Adherence |
|---|---|
| Allocates Memory | No |
| Thread-Safe | No [1] |
| Uses Atomics | No |
| Lock-Free | Yes |
[1] Function is reentrant, but concurrent calls on the same clock object are not safe. Thread-safety is also affected by that of the allocator object associated with the clock object.
- Parameters
-
[in] clock the handle to the clock which is being initialized
- Returns
- RCL_RET_OK if the time source was successfully finalized, or
- RCL_RET_INVALID_ARGUMENT if any arguments are invalid, or
- RCL_RET_ERROR an unspecified error occur.
Definition at line 204 of file time.c.
References RCL_RET_ERROR, RCL_RET_INVALID_ARGUMENT, RCL_RET_OK, RCL_STEADY_TIME, and rcl_clock_s::type.
Referenced by rcl_clock_fini().
◆ rcl_steady_clock_init()
| RCL_PUBLIC RCL_WARN_UNUSED rcl_ret_t rcl_steady_clock_init | ( | rcl_clock_t * | clock, |
| rcl_allocator_t * | allocator | ||
| ) |
Initialize a clock as a RCL_STEADY_TIME time source.
This will allocate all necessary internal structures, and initialize variables. It is specifically setting up a RCL_STEADY_TIME time source.
| Attribute | Adherence |
|---|---|
| Allocates Memory | No |
| Thread-Safe | No [1] |
| Uses Atomics | No |
| Lock-Free | Yes |
[1] Function is reentrant, but concurrent calls on the same clock object are not safe. Thread-safety is also affected by that of the allocator object.
- Parameters
-
[in] clock the handle to the clock which is being initialized [in] allocator The allocator to use for allocations
- Returns
- RCL_RET_OK if the time source was successfully initialized, or
- RCL_RET_INVALID_ARGUMENT if any arguments are invalid, or
- RCL_RET_ERROR an unspecified error occur.
Definition at line 191 of file time.c.
References rcl_clock_s::get_now, RCL_RET_INVALID_ARGUMENT, RCL_RET_OK, RCL_STEADY_TIME, and rcl_clock_s::type.
Referenced by rcl_clock_init().
◆ rcl_system_clock_fini()
| RCL_PUBLIC RCL_WARN_UNUSED rcl_ret_t rcl_system_clock_fini | ( | rcl_clock_t * | clock | ) |
Finalize a clock as a RCL_SYSTEM_TIME time source.
Finalize the clock as a RCL_SYSTEM_TIME time source.
This will deallocate all necessary internal structures, and clean up any variables. It is specifically setting up a system time source. It is expected to be paired with the init fuction.
This function is not thread-safe with any function operating on the same clock object.
| Attribute | Adherence |
|---|---|
| Allocates Memory | No |
| Thread-Safe | No [1] |
| Uses Atomics | No |
| Lock-Free | Yes |
[1] Function is reentrant, but concurrent calls on the same clock object are not safe. Thread-safety is also affected by that of the allocator object associated with the clock object.
- Parameters
-
[in] clock the handle to the clock which is being initialized.
- Returns
- RCL_RET_OK if the time source was successfully finalized, or
- RCL_RET_INVALID_ARGUMENT if any arguments are invalid, or
- RCL_RET_ERROR an unspecified error occur.
Definition at line 230 of file time.c.
References RCL_RET_ERROR, RCL_RET_INVALID_ARGUMENT, RCL_RET_OK, RCL_SYSTEM_TIME, and rcl_clock_s::type.
Referenced by rcl_clock_fini().
◆ rcl_system_clock_init()
| RCL_PUBLIC RCL_WARN_UNUSED rcl_ret_t rcl_system_clock_init | ( | rcl_clock_t * | clock, |
| rcl_allocator_t * | allocator | ||
| ) |
Initialize a clock as a RCL_SYSTEM_TIME time source.
Initialize the clock as a RCL_SYSTEM_TIME time source.
This will allocate all necessary internal structures, and initialize variables. It is specifically setting up a system time source.
| Attribute | Adherence |
|---|---|
| Allocates Memory | No |
| Thread-Safe | No [1] |
| Uses Atomics | No |
| Lock-Free | Yes |
[1] Function is reentrant, but concurrent calls on the same clock object are not safe. Thread-safety is also affected by that of the allocator object associated with the clock object.
- Parameters
-
[in] clock the handle to the clock which is being initialized [in] allocator The allocator to use for allocations
- Returns
- RCL_RET_OK if the time source was successfully initialized, or
- RCL_RET_INVALID_ARGUMENT if any arguments are invalid, or
- RCL_RET_ERROR an unspecified error occur.
Definition at line 217 of file time.c.
References rcl_clock_s::get_now, RCL_RET_INVALID_ARGUMENT, RCL_RET_OK, RCL_SYSTEM_TIME, and rcl_clock_s::type.
Referenced by rcl_clock_init().