Coordinate the order and timing of available communication tasks. More...
#include <rclcpp/executor.hpp>
Public Member Functions | |
| RCLCPP_PUBLIC | Executor (const rclcpp::ExecutorOptions &options=rclcpp::ExecutorOptions()) |
| Default constructor. More... | |
| virtual RCLCPP_PUBLIC | ~Executor () |
| Default destructor. | |
| virtual void | spin ()=0 |
| Do work periodically as it becomes available to us. Blocking call, may block indefinitely. | |
| virtual RCLCPP_PUBLIC void | add_callback_group (rclcpp::CallbackGroup::SharedPtr group_ptr, rclcpp::node_interfaces::NodeBaseInterface::SharedPtr node_ptr, bool notify=true) |
| Add a callback group to an executor. More... | |
| virtual RCLCPP_PUBLIC std::vector< rclcpp::CallbackGroup::WeakPtr > | get_all_callback_groups () |
| Get callback groups that belong to executor. More... | |
| virtual RCLCPP_PUBLIC std::vector< rclcpp::CallbackGroup::WeakPtr > | get_manually_added_callback_groups () |
| Get callback groups that belong to executor. More... | |
| virtual RCLCPP_PUBLIC std::vector< rclcpp::CallbackGroup::WeakPtr > | get_automatically_added_callback_groups_from_nodes () |
| Get callback groups that belong to executor. More... | |
| virtual RCLCPP_PUBLIC void | remove_callback_group (rclcpp::CallbackGroup::SharedPtr group_ptr, bool notify=true) |
| Remove a callback group from the executor. More... | |
| virtual RCLCPP_PUBLIC void | add_node (rclcpp::node_interfaces::NodeBaseInterface::SharedPtr node_ptr, bool notify=true) |
| Add a node to the executor. More... | |
| virtual RCLCPP_PUBLIC void | add_node (std::shared_ptr< rclcpp::Node > node_ptr, bool notify=true) |
| Convenience function which takes Node and forwards NodeBaseInterface. More... | |
| virtual RCLCPP_PUBLIC void | remove_node (rclcpp::node_interfaces::NodeBaseInterface::SharedPtr node_ptr, bool notify=true) |
| Remove a node from the executor. More... | |
| virtual RCLCPP_PUBLIC void | remove_node (std::shared_ptr< rclcpp::Node > node_ptr, bool notify=true) |
| Convenience function which takes Node and forwards NodeBaseInterface. More... | |
| template<typename RepT = int64_t, typename T = std::milli> | |
| void | spin_node_once (rclcpp::node_interfaces::NodeBaseInterface::SharedPtr node, std::chrono::duration< RepT, T > timeout=std::chrono::duration< RepT, T >(-1)) |
| Add a node to executor, execute the next available unit of work, and remove the node. More... | |
| template<typename NodeT = rclcpp::Node, typename RepT = int64_t, typename T = std::milli> | |
| void | spin_node_once (std::shared_ptr< NodeT > node, std::chrono::duration< RepT, T > timeout=std::chrono::duration< RepT, T >(-1)) |
| Convenience function which takes Node and forwards NodeBaseInterface. | |
| virtual RCLCPP_PUBLIC void | spin_node_some (rclcpp::node_interfaces::NodeBaseInterface::SharedPtr node) |
| Add a node, complete all immediately available work, and remove the node. More... | |
| virtual RCLCPP_PUBLIC void | spin_node_some (std::shared_ptr< rclcpp::Node > node) |
| Convenience function which takes Node and forwards NodeBaseInterface. | |
| virtual RCLCPP_PUBLIC void | spin_some (std::chrono::nanoseconds max_duration=std::chrono::nanoseconds(0)) |
| Collect work once and execute all available work, optionally within a max duration. More... | |
| virtual RCLCPP_PUBLIC void | spin_node_all (rclcpp::node_interfaces::NodeBaseInterface::SharedPtr node, std::chrono::nanoseconds max_duration) |
| Add a node, complete all immediately available work exhaustively, and remove the node. More... | |
| virtual RCLCPP_PUBLIC void | spin_node_all (std::shared_ptr< rclcpp::Node > node, std::chrono::nanoseconds max_duration) |
| Convenience function which takes Node and forwards NodeBaseInterface. | |
| virtual RCLCPP_PUBLIC void | spin_all (std::chrono::nanoseconds max_duration) |
| Collect and execute work repeatedly within a duration or until no more work is available. More... | |
| virtual RCLCPP_PUBLIC void | spin_once (std::chrono::nanoseconds timeout=std::chrono::nanoseconds(-1)) |
| Collect work once and execute the next available work, optionally within a duration. More... | |
| template<typename FutureT , typename TimeRepT = int64_t, typename TimeT = std::milli> | |
| FutureReturnCode | spin_until_future_complete (const FutureT &future, std::chrono::duration< TimeRepT, TimeT > timeout=std::chrono::duration< TimeRepT, TimeT >(-1)) |
| Spin (blocking) until the future is complete, it times out waiting, or rclcpp is interrupted. More... | |
| virtual RCLCPP_PUBLIC void | cancel () |
| Cancel any running spin* function, causing it to return. More... | |
| RCLCPP_PUBLIC bool | is_spinning () |
| Returns true if the executor is currently spinning. More... | |
Protected Member Functions | |
| Executor (const std::shared_ptr< rclcpp::Context > &context) | |
| Constructor that will not initialize any non-trivial members. More... | |
| RCLCPP_PUBLIC void | spin_node_once_nanoseconds (rclcpp::node_interfaces::NodeBaseInterface::SharedPtr node, std::chrono::nanoseconds timeout) |
| Add a node to executor, execute the next available unit of work, and remove the node. More... | |
| virtual RCLCPP_PUBLIC FutureReturnCode | spin_until_future_complete_impl (std::chrono::nanoseconds timeout, const std::function< std::future_status(std::chrono::nanoseconds wait_time)> &wait_for_future) |
| Spin (blocking) until the future is complete, it times out waiting, or rclcpp is interrupted. More... | |
| RCLCPP_PUBLIC void | spin_some_impl (std::chrono::nanoseconds max_duration, bool exhaustive) |
| Collect work and execute available work, optionally within a duration. More... | |
| RCLCPP_PUBLIC void | execute_any_executable (AnyExecutable &any_exec) |
| Find the next available executable and do the work associated with it. More... | |
| RCLCPP_PUBLIC void | collect_entities () |
| Gather all of the waitable entities from associated nodes and callback groups. | |
| RCLCPP_PUBLIC void | wait_for_work (std::chrono::nanoseconds timeout=std::chrono::nanoseconds(-1)) |
| Block until more work becomes avilable or timeout is reached. More... | |
| RCLCPP_PUBLIC bool | get_next_ready_executable (AnyExecutable &any_executable) |
| Check for executable in ready state and populate union structure. More... | |
| RCLCPP_PUBLIC bool | get_next_executable (AnyExecutable &any_executable, std::chrono::nanoseconds timeout=std::chrono::nanoseconds(-1)) |
| Wait for executable in ready state and populate union structure. More... | |
| virtual RCLCPP_PUBLIC void | handle_updated_entities (bool notify) |
| This function triggers a recollect of all entities that are registered to the executor. More... | |
| virtual RCLCPP_PUBLIC void | spin_once_impl (std::chrono::nanoseconds timeout) |
| rclcpp::WaitSet wait_set_ | RCPPUTILS_TSA_GUARDED_BY (mutex_) |
| WaitSet to be waited on. | |
| std::optional< rclcpp::WaitResult< rclcpp::WaitSet > > wait_result_ | RCPPUTILS_TSA_GUARDED_BY (mutex_) |
| rclcpp::executors::ExecutorEntitiesCollection current_collection_ | RCPPUTILS_TSA_GUARDED_BY (mutex_) |
| Hold the current state of the collection being waited on by the waitset. | |
| std::shared_ptr< rclcpp::executors::ExecutorNotifyWaitable > current_notify_waitable_ | RCPPUTILS_TSA_GUARDED_BY (mutex_) |
| Hold the current state of the notify waitable being waited on by the waitset. | |
Static Protected Member Functions | |
| static RCLCPP_PUBLIC void | execute_subscription (rclcpp::SubscriptionBase::SharedPtr subscription) |
| Run subscription executable. More... | |
| static RCLCPP_PUBLIC void | execute_timer (rclcpp::TimerBase::SharedPtr timer, const std::shared_ptr< void > &data_ptr) |
| Run timer executable. More... | |
| static RCLCPP_PUBLIC void | execute_service (rclcpp::ServiceBase::SharedPtr service) |
| Run service server executable. More... | |
| static RCLCPP_PUBLIC void | execute_client (rclcpp::ClientBase::SharedPtr client) |
| Run service client executable. More... | |
Protected Attributes | |
| std::atomic_bool | spinning |
| Spinning state, used to prevent multi threaded calls to spin and to cancel blocking spins. | |
| std::shared_ptr< rclcpp::GuardCondition > | interrupt_guard_condition_ |
| Guard condition for signaling the rmw layer to wake up for special events. | |
| std::shared_ptr< rclcpp::GuardCondition > | shutdown_guard_condition_ |
| Guard condition for signaling the rmw layer to wake up for system shutdown. | |
| std::mutex | mutex_ |
| std::shared_ptr< rclcpp::Context > | context_ |
| The context associated with this executor. | |
| std::shared_ptr< rclcpp::executors::ExecutorNotifyWaitable > | notify_waitable_ |
| Waitable containing guard conditions controlling the executor flow. More... | |
| std::atomic_bool | entities_need_rebuild_ |
| rclcpp::executors::ExecutorEntitiesCollector | collector_ |
| Collector used to associate executable entities from nodes and guard conditions. | |
| rclcpp::OnShutdownCallbackHandle | shutdown_callback_handle_ |
| shutdown callback handle registered to Context | |
| std::unique_ptr< ExecutorImplementation > | impl_ |
| Pointer to implementation. | |
Detailed Description
Coordinate the order and timing of available communication tasks.
Executor provides spin functions (including spin_node_once and spin_some). It coordinates the nodes and callback groups by looking for available work and completing it, based on the threading or concurrency scheme provided by the subclass implementation. An example of available work is executing a subscription callback, or a timer callback. The executor structure allows for a decoupling of the communication graph and the execution model. See SingleThreadedExecutor and MultiThreadedExecutor for examples of execution paradigms.
Definition at line 64 of file executor.hpp.
Constructor & Destructor Documentation
◆ Executor() [1/2]
|
explicit |
Default constructor.
- Parameters
-
[in] options Options used to configure the executor.
Definition at line 61 of file executor.cpp.
◆ Executor() [2/2]
|
explicitprotected |
Constructor that will not initialize any non-trivial members.
This constructor is intended to be used by any derived executor that explicitly does not want to use the default implementation provided by this class.
Definition at line 53 of file executor.cpp.
Member Function Documentation
◆ add_callback_group()
|
virtual |
Add a callback group to an executor.
An executor can have zero or more callback groups which provide work during spin functions. When an executor attempts to add a callback group, the executor checks to see if it is already associated with another executor, and if it has been, then an exception is thrown. Otherwise, the callback group is added to the executor.
Adding a callback group with this method does not associate its node with this executor in any way
- Parameters
-
[in] group_ptr a shared ptr that points to a callback group [in] node_ptr a shared pointer that points to a node base interface [in] notify True to trigger the interrupt guard condition during this function. If the executor is blocked at the rmw layer while waiting for work and it is notified that a new callback group was added, it will wake up.
- Exceptions
-
std::runtime_error if the callback group is associated to an executor
Definition at line 170 of file executor.cpp.
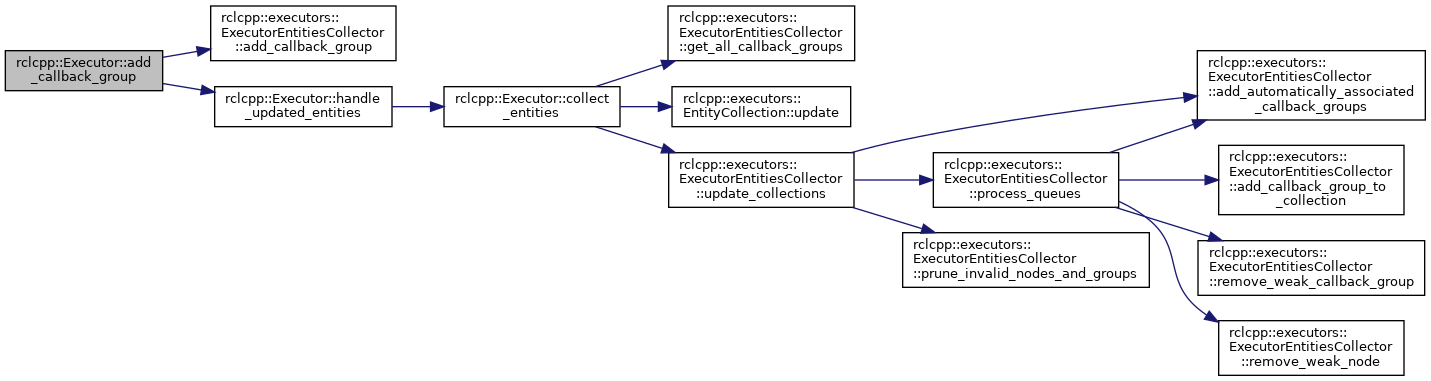
References rclcpp::executors::ExecutorEntitiesCollector::add_callback_group(), collector_, and handle_updated_entities().
◆ add_node() [1/2]
|
virtual |
Add a node to the executor.
Nodes have associated callback groups, and this method adds any of those callback groups to this executor which have their automatically_add_to_executor_with_node parameter true. The node is also associated with the executor so that future callback groups which are created on the node with the automatically_add_to_executor_with_node parameter set to true are also automatically associated with this executor.
Callback groups with the automatically_add_to_executor_with_node parameter set to false must be manually added to an executor using the rclcpp::Executor::add_callback_group method.
If a node is already associated with an executor, this method throws an exception.
- Parameters
-
[in] node_ptr Shared pointer to the node to be added. [in] notify True to trigger the interrupt guard condition during this function. If the executor is blocked at the rmw layer while waiting for work and it is notified that a new node was added, it will wake up.
- Exceptions
-
std::runtime_error if a node is already associated to an executor
Definition at line 187 of file executor.cpp.
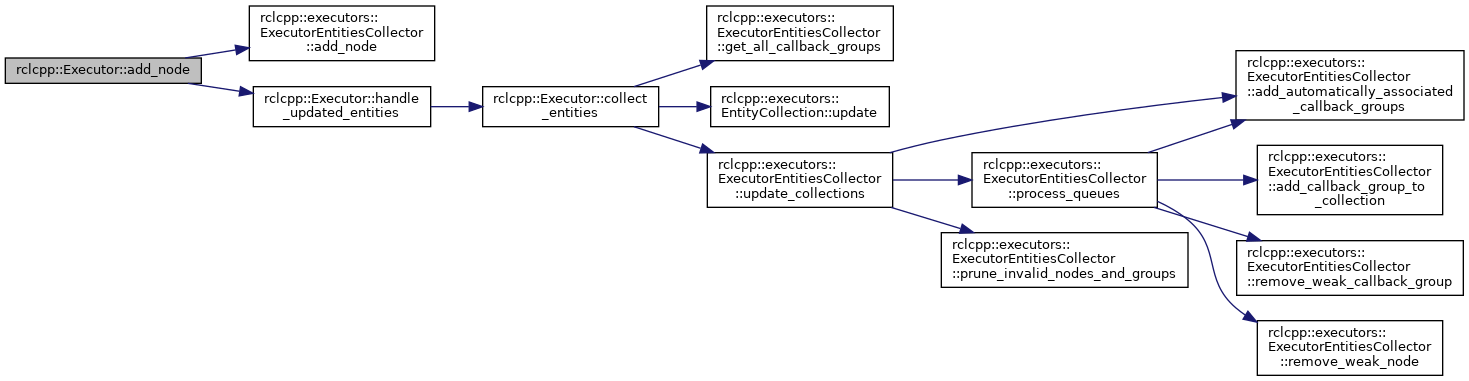
References rclcpp::executors::ExecutorEntitiesCollector::add_node(), collector_, and handle_updated_entities().
Referenced by add_node(), rclcpp::spin(), spin_node_all(), spin_node_once_nanoseconds(), and spin_node_some().
◆ add_node() [2/2]
|
virtual |
Convenience function which takes Node and forwards NodeBaseInterface.
- See also
- rclcpp::Executor::add_node
Definition at line 217 of file executor.cpp.
References add_node().
◆ cancel()
|
virtual |
Cancel any running spin* function, causing it to return.
This function can be called asynchonously from any thread.
- Exceptions
-
std::runtime_error if there is an issue triggering the guard condition
Definition at line 455 of file executor.cpp.
References interrupt_guard_condition_, and spinning.
◆ execute_any_executable()
|
protected |
Find the next available executable and do the work associated with it.
- Parameters
-
[in] any_exec Union structure that can hold any executable type (timer, subscription, service, client).
- Exceptions
-
std::runtime_error if there is an issue triggering the guard condition
Definition at line 467 of file executor.cpp.
References execute_client(), execute_service(), execute_subscription(), execute_timer(), and spinning.
Referenced by rclcpp::executors::SingleThreadedExecutor::spin(), and spin_some_impl().
◆ execute_client()
|
staticprotected |
Run service client executable.
Do necessary setup and tear-down as well as executing the service client callback.
- Parameters
-
[in] service Service to execute
Definition at line 662 of file executor.cpp.
Referenced by execute_any_executable(), and rclcpp::executors::StaticSingleThreadedExecutor::execute_ready_executables().
◆ execute_service()
|
staticprotected |
Run service server executable.
Do necessary setup and tear-down as well as executing the service server callback.
- Parameters
-
[in] service Service to execute
Definition at line 650 of file executor.cpp.
Referenced by execute_any_executable(), and rclcpp::executors::StaticSingleThreadedExecutor::execute_ready_executables().
◆ execute_subscription()
|
staticprotected |
Run subscription executable.
Do necessary setup and tear-down as well as executing the subscription.
- Parameters
-
[in] subscription Subscription to execute
Definition at line 542 of file executor.cpp.
References rclcpp::MessageInfo::get_rmw_message_info().
Referenced by execute_any_executable(), and rclcpp::executors::StaticSingleThreadedExecutor::execute_ready_executables().
◆ execute_timer()
|
staticprotected |
Run timer executable.
Do necessary setup and tear-down as well as executing the timer callback.
- Parameters
-
[in] timer Timer to execute
Definition at line 644 of file executor.cpp.
Referenced by execute_any_executable(), and rclcpp::executors::StaticSingleThreadedExecutor::execute_ready_executables().
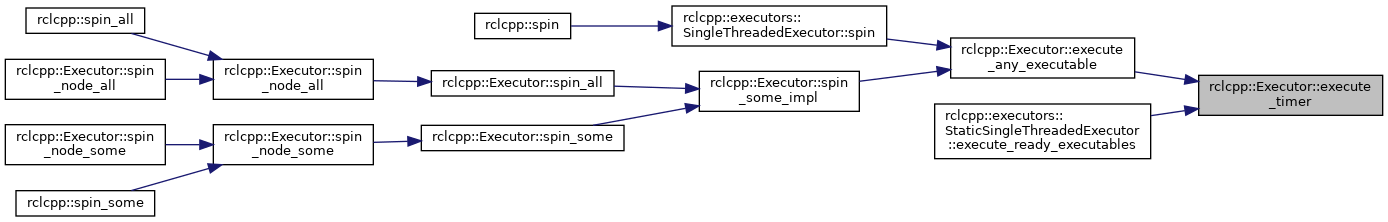
◆ get_all_callback_groups()
|
virtual |
Get callback groups that belong to executor.
This function returns a vector of weak pointers that point to callback groups that were associated with the executor. The callback groups associated with this executor may have been added with add_callback_group, or added when a node was added to the executor with add_node, or automatically added when it created by a node already associated with this executor and the automatically_add_to_executor_with_node parameter was true.
- Returns
- a vector of weak pointers that point to callback groups that are associated with the executor
Definition at line 149 of file executor.cpp.
References collector_, rclcpp::executors::ExecutorEntitiesCollector::get_all_callback_groups(), and rclcpp::executors::ExecutorEntitiesCollector::update_collections().
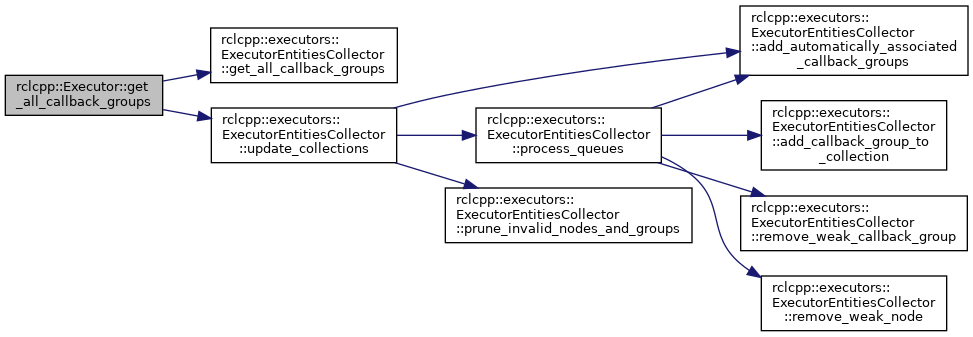
◆ get_automatically_added_callback_groups_from_nodes()
|
virtual |
Get callback groups that belong to executor.
This function returns a vector of weak pointers that point to callback groups that were added from a node that is associated with the executor. The callback groups are added when a node is added to the executor with add_node, or automatically if they are created in the future by that node and have the automatically_add_to_executor_with_node argument set to true.
- Returns
- a vector of weak pointers that point to callback groups from a node associated with the executor
Definition at line 163 of file executor.cpp.
References collector_, rclcpp::executors::ExecutorEntitiesCollector::get_automatically_added_callback_groups(), and rclcpp::executors::ExecutorEntitiesCollector::update_collections().
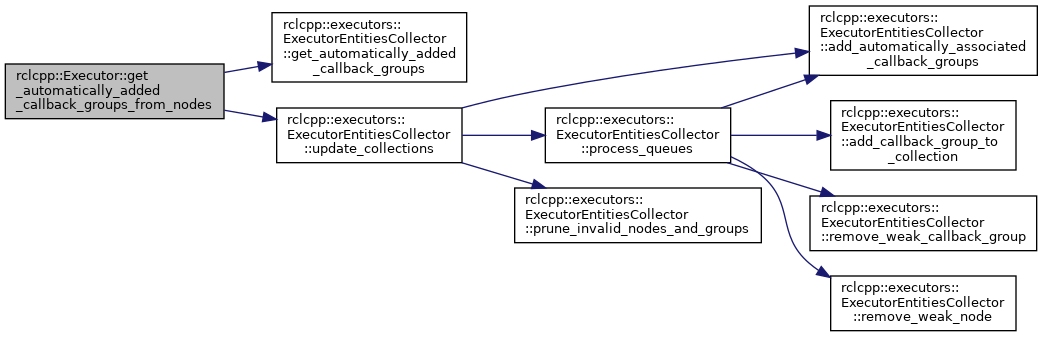
◆ get_manually_added_callback_groups()
|
virtual |
Get callback groups that belong to executor.
This function returns a vector of weak pointers that point to callback groups that were associated with the executor. The callback groups associated with this executor have been added with add_callback_group.
- Returns
- a vector of weak pointers that point to callback groups that are associated with the executor
Definition at line 156 of file executor.cpp.
References collector_, rclcpp::executors::ExecutorEntitiesCollector::get_manually_added_callback_groups(), and rclcpp::executors::ExecutorEntitiesCollector::update_collections().
◆ get_next_executable()
|
protected |
Wait for executable in ready state and populate union structure.
If an executable is ready, it will return immediately, otherwise block based on the timeout for work to become ready.
- Parameters
-
[out] any_executable populated union structure of ready executable [in] timeout duration of time to wait for work, a negative value (the defualt behavior), will make this function block indefinitely
- Returns
- true if an executable was ready and any_executable was populated, otherwise false
Definition at line 897 of file executor.cpp.
References get_next_ready_executable(), spinning, and wait_for_work().
Referenced by rclcpp::executors::SingleThreadedExecutor::spin().
◆ get_next_ready_executable()
|
protected |
Check for executable in ready state and populate union structure.
- Parameters
-
[out] any_executable populated union structure of ready executable
- Returns
- true if an executable was ready and any_executable was populated, otherwise false
Definition at line 774 of file executor.cpp.
Referenced by get_next_executable(), and spin_some_impl().
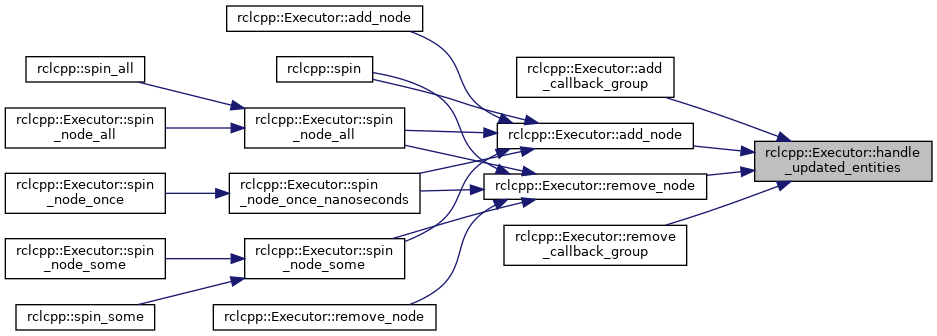
◆ handle_updated_entities()
|
protectedvirtual |
This function triggers a recollect of all entities that are registered to the executor.
Calling this function is thread safe.
- Parameters
-
[in] notify if true will execute a trigger that will wake up a waiting executor
Reimplemented in rclcpp::experimental::executors::EventsExecutor.
Definition at line 134 of file executor.cpp.
References collect_entities(), interrupt_guard_condition_, and spinning.
Referenced by add_callback_group(), add_node(), remove_callback_group(), and remove_node().
◆ is_spinning()
| bool Executor::is_spinning | ( | ) |
Returns true if the executor is currently spinning.
This function can be called asynchronously from any thread.
- Returns
- True if the executor is currently spinning.
Definition at line 917 of file executor.cpp.
References spinning.
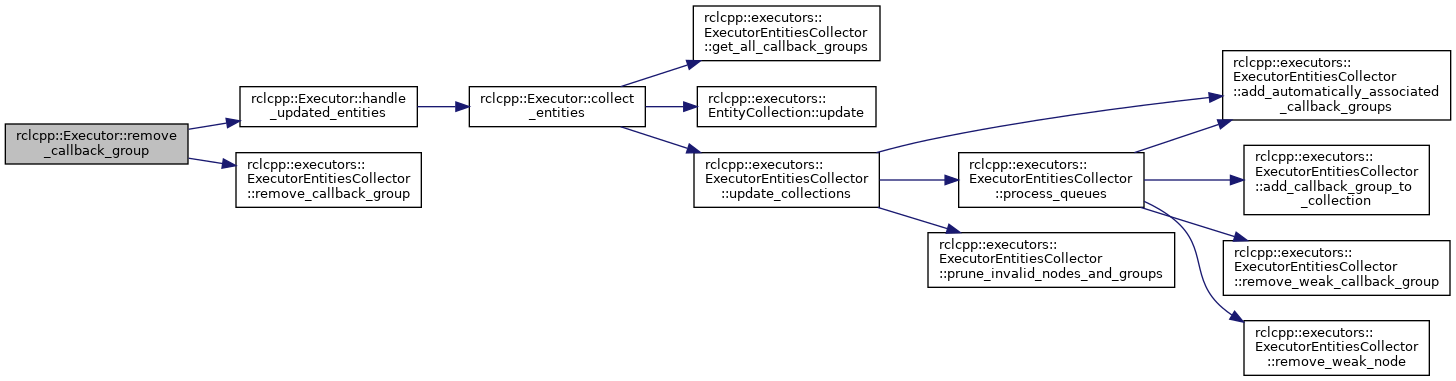
◆ remove_callback_group()
|
virtual |
Remove a callback group from the executor.
The callback group is removed from and disassociated with the executor. If the callback group removed was the last callback group from the node that is associated with the executor, the interrupt guard condition is triggered and node's guard condition is removed from the executor.
This function only removes a callback group that was manually added with rclcpp::Executor::add_callback_group. To remove callback groups that were added from a node using rclcpp::Executor::add_node, use rclcpp::Executor::remove_node instead.
- Parameters
-
[in] group_ptr Shared pointer to the callback group to be added. [in] notify True to trigger the interrupt guard condition during this function. If the executor is blocked at the rmw layer while waiting for work and it is notified that a callback group was removed, it will wake up.
- Exceptions
-
std::runtime_error if node is deleted before callback group std::runtime_error if the callback group is not associated with the executor
Definition at line 201 of file executor.cpp.
References collector_, handle_updated_entities(), and rclcpp::executors::ExecutorEntitiesCollector::remove_callback_group().
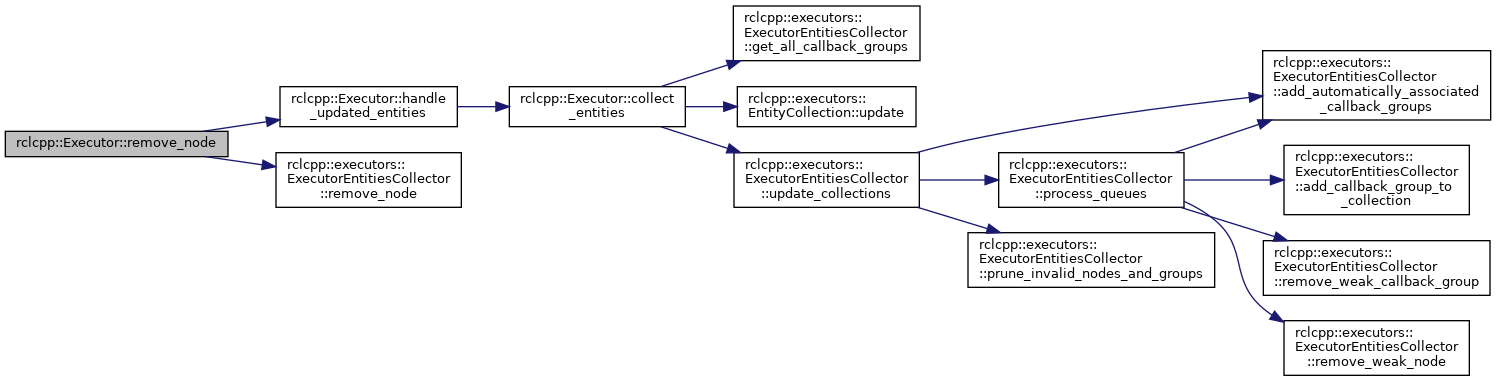
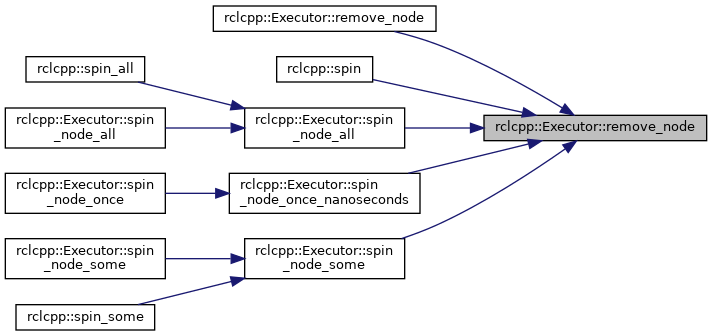
◆ remove_node() [1/2]
|
virtual |
Remove a node from the executor.
Any callback groups automatically added when this node was added with rclcpp::Executor::add_node are automatically removed, and the node is no longer associated with this executor.
This also means that future callback groups created by the given node are no longer automatically added to this executor.
- Parameters
-
[in] node_ptr Shared pointer to the node to remove. [in] notify True to trigger the interrupt guard condition and wake up the executor. This is useful if the last node was removed from the executor while the executor was blocked waiting for work in another thread, because otherwise the executor would never be notified.
- Exceptions
-
std::runtime_error if the node is not associated with an executor. std::runtime_error if the node is not associated with this executor.
Definition at line 223 of file executor.cpp.
References collector_, handle_updated_entities(), and rclcpp::executors::ExecutorEntitiesCollector::remove_node().
Referenced by remove_node(), rclcpp::spin(), spin_node_all(), spin_node_once_nanoseconds(), and spin_node_some().
◆ remove_node() [2/2]
|
virtual |
Convenience function which takes Node and forwards NodeBaseInterface.
- See also
- rclcpp::Executor::remove_node
Definition at line 237 of file executor.cpp.
References remove_node().
◆ spin_all()
|
virtual |
Collect and execute work repeatedly within a duration or until no more work is available.
This function can be overridden. The default implementation is suitable for a single-threaded model of execution. Adding subscriptions, timers, services, etc. with blocking callbacks will cause this function to block (which may have unintended consequences). If the time that waitables take to be executed is longer than the period on which new waitables become ready, this method will execute work repeatedly until max_duration has elapsed.
- Parameters
-
[in] max_duration The maximum amount of time to spend executing work, must be >= 0. 0is potentially block forever until no more work is available.
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argument if max_duration is less than 0. Note that spin_all() may take longer than this time as it only returns once max_duration has been exceeded.
Reimplemented in rclcpp::experimental::executors::EventsExecutor, and rclcpp::executors::StaticSingleThreadedExecutor.
Definition at line 341 of file executor.cpp.
References spin_some_impl().
Referenced by spin_node_all().

◆ spin_node_all()
|
virtual |
Add a node, complete all immediately available work exhaustively, and remove the node.
- Parameters
-
[in] node Shared pointer to the node to add.
Definition at line 326 of file executor.cpp.
References add_node(), remove_node(), and spin_all().
Referenced by rclcpp::spin_all(), and spin_node_all().
◆ spin_node_once()
|
inline |
Add a node to executor, execute the next available unit of work, and remove the node.
- Parameters
-
[in] node Shared pointer to the node to add. [in] timeout How long to wait for work to become available. Negative values cause spin_node_once to block indefinitely (the default behavior). A timeout of 0 causes this function to be non-blocking.
Definition at line 247 of file executor.hpp.
References spin_node_once_nanoseconds().
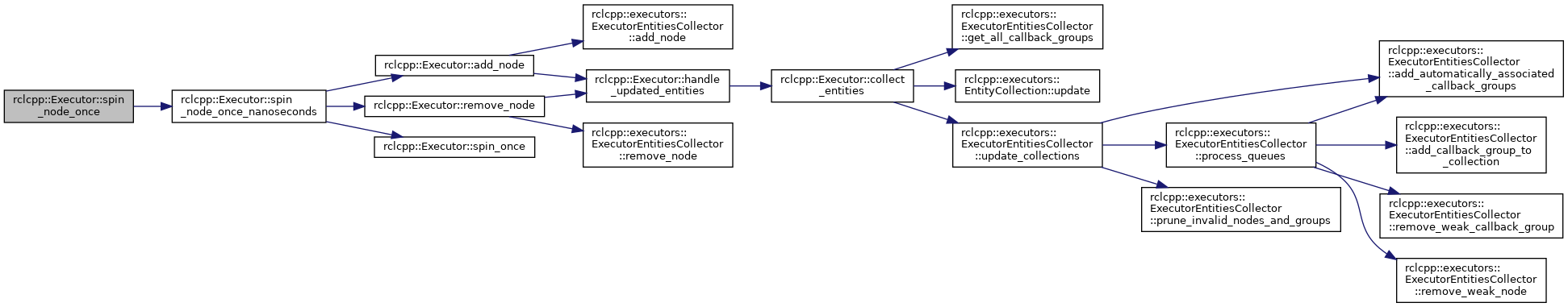
◆ spin_node_once_nanoseconds()
|
protected |
Add a node to executor, execute the next available unit of work, and remove the node.
Implementation of spin_node_once using std::chrono::nanoseconds
- Parameters
-
[in] node Shared pointer to the node to add. [in] timeout How long to wait for work to become available. Negative values cause spin_node_once to block indefinitely (the default behavior). A timeout of 0 causes this function to be non-blocking.
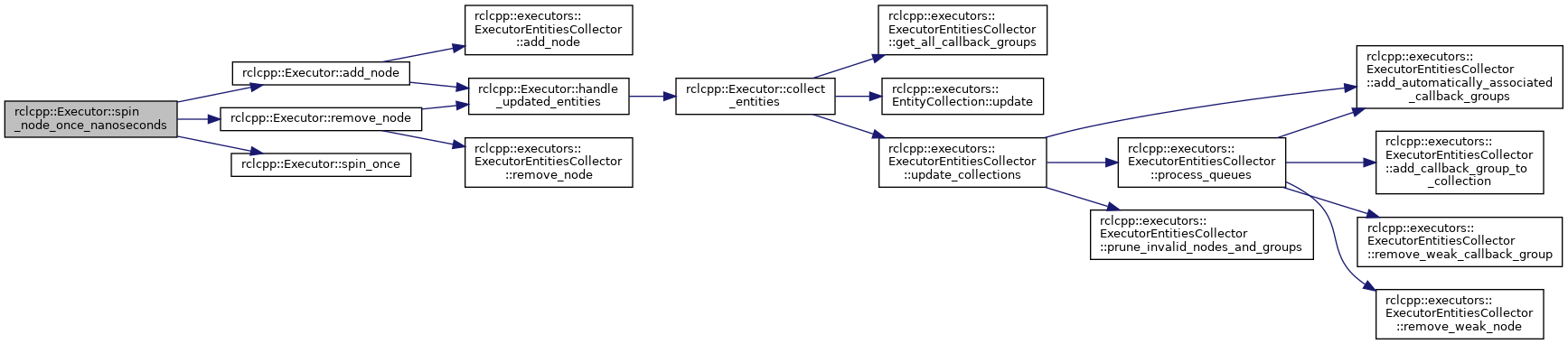
Definition at line 243 of file executor.cpp.
References add_node(), remove_node(), and spin_once().
Referenced by spin_node_once().
◆ spin_node_some()
|
virtual |
Add a node, complete all immediately available work, and remove the node.
- Parameters
-
[in] node Shared pointer to the node to add.
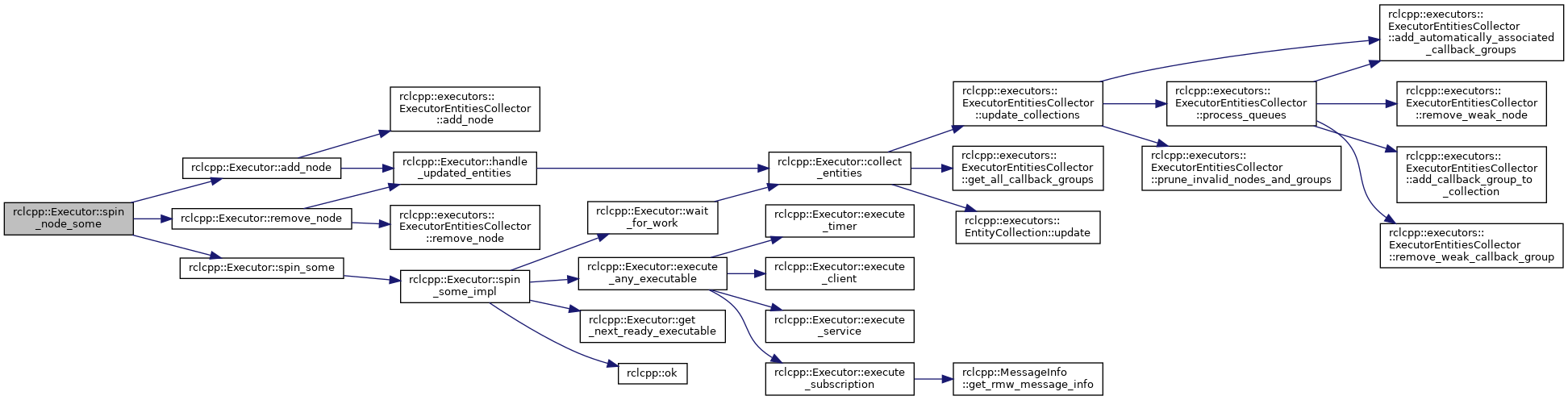
Definition at line 307 of file executor.cpp.
References add_node(), remove_node(), and spin_some().
Referenced by spin_node_some(), and rclcpp::spin_some().
◆ spin_once()
|
virtual |
Collect work once and execute the next available work, optionally within a duration.
This function can be overridden. The default implementation is suitable for a single-thread model of execution. Adding subscriptions, timers, services, etc. with blocking callbacks will cause this function to block (which may have unintended consequences).
- Parameters
-
[in] timeout The maximum amount of time to spend waiting for work. -1is potentially block forever waiting for work.
Definition at line 445 of file executor.cpp.
References spinning.
Referenced by rclcpp::executors::StaticSingleThreadedExecutor::execute_ready_executables(), and spin_node_once_nanoseconds().

◆ spin_some()
|
virtual |
Collect work once and execute all available work, optionally within a max duration.
This function can be overridden. The default implementation is suitable for a single-threaded model of execution. Adding subscriptions, timers, services, etc. with blocking or long running callbacks may cause the function exceed the max_duration significantly.
Work that is ready to be done is collected only once, and when collecting that work entities which may have multiple pieces of work ready will only be executed at most one time. The reason for this is that it is not possible to tell if, for example, a ready subscription has only one message ready or multiple without checking again. Because, in order to find out if there are multiple messages, one message must be taken and executed before checking again if that subscription is still ready. However, this function only checks for ready entities to work on once, and so it will never execute a single entity more than once per call to this function. See spin_all() variants for a function that will repeatedly work on a single entity in a single call.
If there is no work to be done when this called, it will return immediately because the collecting of available work is non-blocking. Before each piece of ready work is executed this function checks if the max_duration has been exceeded, and if it has it returns without starting the execution of the next piece of work.
If a max_duration of 0 is given, then all of the collected work will be executed before the function returns.
- Parameters
-
[in] max_duration The maximum amount of time to spend executing work, or 0 for no limit.
Reimplemented in rclcpp::experimental::executors::EventsExecutor, and rclcpp::executors::StaticSingleThreadedExecutor.
Definition at line 320 of file executor.cpp.
References spin_some_impl().
Referenced by spin_node_some().
◆ spin_some_impl()
|
protected |
Collect work and execute available work, optionally within a duration.
Implementation of spin_some and spin_all. The exhaustive flag controls if the function will re-collect available work within the duration.
- Parameters
-
[in] max_duration The maximum amount of time to spend executing work, or 0 for no limit. [in] exhaustive when set to true, continue to collect work and execute (spin_all) when set to false, return when all collected work is executed (spin_some)
Definition at line 350 of file executor.cpp.
References context_, execute_any_executable(), get_next_ready_executable(), rclcpp::ok(), spinning, and wait_for_work().
Referenced by spin_all(), and spin_some().
◆ spin_until_future_complete()
|
inline |
Spin (blocking) until the future is complete, it times out waiting, or rclcpp is interrupted.
- Parameters
-
[in] future The future to wait on. If this function returns SUCCESS, the future can be accessed without blocking (though it may still throw an exception). [in] timeout Optional timeout parameter, which gets passed to Executor::spin_node_once. -1is block forever,0is non-blocking. If the time spent inside the blocking loop exceeds this timeout, return a TIMEOUT return code.
- Returns
- The return code, one of
SUCCESS,INTERRUPTED, orTIMEOUT.
Definition at line 377 of file executor.hpp.
References spin_until_future_complete_impl().
◆ spin_until_future_complete_impl()
|
protectedvirtual |
Spin (blocking) until the future is complete, it times out waiting, or rclcpp is interrupted.
- See also
- spin_until_future_complete() The only difference with spin_until_future_complete() is that the future's type is obscured through a std::function which lets you wait on it reguardless of type.
- Parameters
-
[in] timeout see spin_until_future_complete() for details [in] wait_for_future function to wait on the future and get the status after waiting
Definition at line 254 of file executor.cpp.
Referenced by spin_until_future_complete().
◆ wait_for_work()
|
protected |
Block until more work becomes avilable or timeout is reached.
Builds a set of waitable entities, which are passed to the middleware. After building wait set, waits on middleware to notify.
- Parameters
-
[in] timeout duration to wait for new work to become available.
- Exceptions
-
std::runtime_error if the wait set can be cleared
Definition at line 742 of file executor.cpp.
References collect_entities().
Referenced by get_next_executable(), and spin_some_impl().
Member Data Documentation
◆ notify_waitable_
|
protected |
Waitable containing guard conditions controlling the executor flow.
This waitable contains the interrupt and shutdown guard condition, as well as the guard condition associated with each node and callback group. By default, if any change is detected in the monitored entities, the notify waitable will awake the executor and rebuild the collections.
Definition at line 587 of file executor.hpp.
Referenced by collect_entities(), rclcpp::experimental::executors::EventsExecutor::~EventsExecutor(), and ~Executor().
The documentation for this class was generated from the following files:
- rclcpp/include/rclcpp/executor.hpp
- rclcpp/src/rclcpp/executor.cpp