#include "rosidl_runtime_c/service_type_support_struct.h"#include "rcl/allocator.h"#include "rcl/event_callback.h"#include "rcl/macros.h"#include "rcl/node.h"#include "rcl/publisher.h"#include "rcl/service_introspection.h"#include "rcl/time.h"#include "rcl/visibility_control.h"#include "rmw/types.h"
Go to the source code of this file.
Classes | |
| struct | rcl_service_s |
| Structure which encapsulates a ROS Service. More... | |
| struct | rcl_service_options_s |
| Options available for a rcl service. More... | |
Typedefs | |
| typedef struct rcl_service_impl_s | rcl_service_impl_t |
| Internal rcl implementation struct. | |
| typedef struct rcl_service_s | rcl_service_t |
| Structure which encapsulates a ROS Service. | |
| typedef struct rcl_service_options_s | rcl_service_options_t |
| Options available for a rcl service. | |
Functions | |
| RCL_PUBLIC RCL_WARN_UNUSED rcl_service_t | rcl_get_zero_initialized_service (void) |
Return a rcl_service_t struct with members set to NULL. More... | |
| RCL_PUBLIC RCL_WARN_UNUSED rcl_ret_t | rcl_service_init (rcl_service_t *service, const rcl_node_t *node, const rosidl_service_type_support_t *type_support, const char *service_name, const rcl_service_options_t *options) |
| Initialize a rcl service. More... | |
| RCL_PUBLIC RCL_WARN_UNUSED rcl_ret_t | rcl_service_fini (rcl_service_t *service, rcl_node_t *node) |
| Finalize a rcl_service_t. More... | |
| RCL_PUBLIC RCL_WARN_UNUSED rcl_service_options_t | rcl_service_get_default_options (void) |
| Return the default service options in a rcl_service_options_t. More... | |
| RCL_PUBLIC RCL_WARN_UNUSED rcl_ret_t | rcl_take_request_with_info (const rcl_service_t *service, rmw_service_info_t *request_header, void *ros_request) |
| Take a pending ROS request using a rcl service. More... | |
| RCL_PUBLIC RCL_WARN_UNUSED rcl_ret_t | rcl_take_request (const rcl_service_t *service, rmw_request_id_t *request_header, void *ros_request) |
| Backwards compatibility function to take a pending ROS request using a rcl service. More... | |
| RCL_PUBLIC RCL_WARN_UNUSED rcl_ret_t | rcl_send_response (const rcl_service_t *service, rmw_request_id_t *response_header, void *ros_response) |
| Send a ROS response to a client using a service. More... | |
| RCL_PUBLIC RCL_WARN_UNUSED const char * | rcl_service_get_service_name (const rcl_service_t *service) |
| Get the topic name for the service. More... | |
| RCL_PUBLIC RCL_WARN_UNUSED const rcl_service_options_t * | rcl_service_get_options (const rcl_service_t *service) |
| Return the rcl service options. More... | |
| RCL_PUBLIC RCL_WARN_UNUSED rmw_service_t * | rcl_service_get_rmw_handle (const rcl_service_t *service) |
| Return the rmw service handle. More... | |
| RCL_PUBLIC bool | rcl_service_is_valid (const rcl_service_t *service) |
| Check that the service is valid. More... | |
| RCL_PUBLIC RCL_WARN_UNUSED const rmw_qos_profile_t * | rcl_service_request_subscription_get_actual_qos (const rcl_service_t *service) |
| Get the actual qos settings of the service's request subscription. More... | |
| RCL_PUBLIC RCL_WARN_UNUSED const rmw_qos_profile_t * | rcl_service_response_publisher_get_actual_qos (const rcl_service_t *service) |
| Get the actual qos settings of the service's response publisher. More... | |
| RCL_PUBLIC RCL_WARN_UNUSED rcl_ret_t | rcl_service_set_on_new_request_callback (const rcl_service_t *service, rcl_event_callback_t callback, const void *user_data) |
| Set the on new request callback function for the service. More... | |
| RCL_PUBLIC RCL_WARN_UNUSED rcl_ret_t | rcl_service_configure_service_introspection (rcl_service_t *service, rcl_node_t *node, rcl_clock_t *clock, const rosidl_service_type_support_t *type_support, const rcl_publisher_options_t publisher_options, rcl_service_introspection_state_t introspection_state) |
| Configure service introspection features for the service. More... | |
Function Documentation
◆ rcl_get_zero_initialized_service()
| RCL_PUBLIC RCL_WARN_UNUSED rcl_service_t rcl_get_zero_initialized_service | ( | void | ) |
Return a rcl_service_t struct with members set to NULL.
Should be called to get a null rcl_service_t before passing to rcl_service_init().
- Returns
- A structure with a zero initialized service.
Definition at line 55 of file service.c.
Referenced by rclcpp::GenericService::GenericService(), and rclcpp::Service< ServiceT >::Service().
◆ rcl_send_response()
| RCL_PUBLIC RCL_WARN_UNUSED rcl_ret_t rcl_send_response | ( | const rcl_service_t * | service, |
| rmw_request_id_t * | response_header, | ||
| void * | ros_response | ||
| ) |
Send a ROS response to a client using a service.
It is the job of the caller to ensure that the type of the ros_response parameter and the type associate with the service (via the type support) match. Passing a different type to send_response produces undefined behavior and cannot be checked by this function and therefore no deliberate error will occur.
send_response() is an non-blocking call.
The ROS response message given by the ros_response void pointer is always owned by the calling code, but should remain constant during rcl_send_response().
This function is thread safe so long as access to both the service and the ros_response is synchronized. That means that calling rcl_send_response() from multiple threads is allowed, but calling rcl_send_response() at the same time as non-thread safe service functions is not, e.g. calling rcl_send_response() and rcl_service_fini() concurrently is not allowed. The message cannot change during the rcl_send_response() call. Before calling rcl_send_response() the message can change but after calling rcl_send_response() it depends on RMW implementation behavior. The same ros_response, however, can be passed to multiple calls of rcl_send_response() simultaneously, even if the services differ. The ros_response is unmodified by rcl_send_response().
| Attribute | Adherence |
|---|---|
| Allocates Memory | No |
| Thread-Safe | Yes [1] |
| Uses Atomics | No |
| Lock-Free | Yes |
[1] for unique pairs of services and responses, see above for more
- Parameters
-
[in] service handle to the service which will make the response [in,out] response_header ptr to the struct holding metadata about the request ID [in] ros_response type-erased pointer to the ROS response message
- Returns
- RCL_RET_OK if the response was sent successfully, or
- RCL_RET_INVALID_ARGUMENT if any arguments are invalid, or
- RCL_RET_SERVICE_INVALID if the service is invalid, or
- RCL_RET_TIMEOUT if a response reader is not ready yet, or
- RCL_RET_ERROR if an unspecified error occurs.
Definition at line 384 of file service.c.
References rcl_service_s::impl, RCL_RET_ERROR, RCL_RET_INVALID_ARGUMENT, RCL_RET_OK, RCL_RET_SERVICE_INVALID, RCL_RET_TIMEOUT, rcl_service_get_options(), and rcl_service_is_valid().

◆ rcl_service_configure_service_introspection()
| RCL_PUBLIC RCL_WARN_UNUSED rcl_ret_t rcl_service_configure_service_introspection | ( | rcl_service_t * | service, |
| rcl_node_t * | node, | ||
| rcl_clock_t * | clock, | ||
| const rosidl_service_type_support_t * | type_support, | ||
| const rcl_publisher_options_t | publisher_options, | ||
| rcl_service_introspection_state_t | introspection_state | ||
| ) |
Configure service introspection features for the service.
Enables or disables service introspection features for this service. If the introspection state is RCL_SERVICE_INTROSPECTION_OFF, then introspection will be disabled. If the state is RCL_SERVICE_INTROSPECTION_METADATA, the client metadata will be published. If the state is RCL_SERVICE_INTROSPECTION_CONTENTS, then the client metadata and service request and response contents will be published.
| Attribute | Adherence |
|---|---|
| Allocates Memory | Yes |
| Thread-Safe | No |
| Uses Atomics | Maybe [1] |
| Lock-Free | Maybe [1] |
[1] rmw implementation defined
- Parameters
-
[in] service service on which to configure service introspection [in] node valid rcl_node_t to use to create the introspection publisher [in] clock valid rcl_clock_t to use to generate the introspection timestamps [in] type_support type support library associated with this service [in] publisher_options options to use when creating the introspection publisher [in] introspection_state rcl_service_introspection_state_t describing whether introspection should be OFF, METADATA, or CONTENTS
- Returns
- RCL_RET_OK if the call was successful, or
- RCL_RET_ERROR if the event publisher is invalid, or
- RCL_RET_NODE_INVALID if the given node is invalid, or
- RCL_RET_INVALID_ARGUMENT if the client or node structure is invalid,
- RCL_RET_BAD_ALLOC if a memory allocation failed
Definition at line 471 of file service.c.
References rcl_service_options_s::allocator, rcl_service_s::impl, RCL_RET_BAD_ALLOC, RCL_RET_INVALID_ARGUMENT, RCL_RET_OK, RCL_RET_SERVICE_INVALID, and rcl_service_is_valid().
Referenced by rclcpp::Service< ServiceT >::configure_introspection().
◆ rcl_service_fini()
| RCL_PUBLIC RCL_WARN_UNUSED rcl_ret_t rcl_service_fini | ( | rcl_service_t * | service, |
| rcl_node_t * | node | ||
| ) |
Finalize a rcl_service_t.
After calling, the node will no longer listen for requests for this service. (assuming this is the only service of this type in this node).
After calling, calls to rcl_wait(), rcl_take_request(), and rcl_send_response() will fail when using this service. Additionally rcl_wait() will be interrupted if currently blocking. However, the given node handle is still valid.
| Attribute | Adherence |
|---|---|
| Allocates Memory | Yes |
| Thread-Safe | No |
| Uses Atomics | No |
| Lock-Free | Yes |
- Parameters
-
[in,out] service handle to the service to be deinitialized [in] node a valid (not finalized) handle to the node used to create the service
- Returns
- RCL_RET_OK if service was deinitialized successfully, or
- RCL_RET_INVALID_ARGUMENT if any arguments are invalid, or
- RCL_RET_SERVICE_INVALID if the service is invalid, or
- RCL_RET_NODE_INVALID if the node is invalid, or
- RCL_RET_ERROR if an unspecified error occurs.
Definition at line 234 of file service.c.
References rcl_service_options_s::allocator, rcl_service_s::impl, rcl_node_get_rmw_handle(), rcl_node_is_valid_except_context(), RCL_RET_ERROR, RCL_RET_INVALID_ARGUMENT, RCL_RET_NODE_INVALID, RCL_RET_OK, and RCL_RET_SERVICE_INVALID.
Referenced by rclcpp::GenericService::GenericService(), and rclcpp::Service< ServiceT >::Service().
◆ rcl_service_get_default_options()
| RCL_PUBLIC RCL_WARN_UNUSED rcl_service_options_t rcl_service_get_default_options | ( | void | ) |
Return the default service options in a rcl_service_options_t.
The defaults are:
- qos = rmw_qos_profile_services_default
- allocator = rcl_get_default_allocator()
Definition at line 286 of file service.c.
References rcl_service_options_s::allocator, rcl_service_options_s::qos, and rcl_get_default_allocator.
Referenced by rclcpp::create_generic_service(), rclcpp::create_service(), and rcl_node_type_description_service_init().
◆ rcl_service_get_options()
| RCL_PUBLIC RCL_WARN_UNUSED const rcl_service_options_t* rcl_service_get_options | ( | const rcl_service_t * | service | ) |
Return the rcl service options.
This function returns the service's internal options struct. This function can fail, and therefore return NULL, if the:
- service is
NULL - service is invalid (never called init, called fini, or invalid)
The returned struct is only valid as long as the service is valid. The values in the struct may change if the service's options change, and therefore copying the struct is recommended if this is a concern.
| Attribute | Adherence |
|---|---|
| Allocates Memory | No |
| Thread-Safe | No |
| Uses Atomics | No |
| Lock-Free | Yes |
- Parameters
-
[in] service pointer to the service
- Returns
- options struct if successful, otherwise
NULL
Definition at line 308 of file service.c.
References rcl_service_s::impl, and rcl_service_is_valid().
Referenced by rcl_send_response(), rcl_service_get_service_name(), and rcl_take_request_with_info().

◆ rcl_service_get_rmw_handle()
| RCL_PUBLIC RCL_WARN_UNUSED rmw_service_t* rcl_service_get_rmw_handle | ( | const rcl_service_t * | service | ) |
Return the rmw service handle.
The handle returned is a pointer to the internally held rmw handle. This function can fail, and therefore return NULL, if the:
- service is
NULL - service is invalid (never called init, called fini, or invalid)
The returned handle is made invalid if the service is finalized or if rcl_shutdown() is called. The returned handle is not guaranteed to be valid for the life time of the service as it may be finalized and recreated itself. Therefore it is recommended to get the handle from the service using this function each time it is needed and avoid use of the handle concurrently with functions that might change it.
| Attribute | Adherence |
|---|---|
| Allocates Memory | No |
| Thread-Safe | No |
| Uses Atomics | No |
| Lock-Free | Yes |
- Parameters
-
[in] service pointer to the rcl service
- Returns
- rmw service handle if successful, otherwise
NULL
Definition at line 317 of file service.c.
References rcl_service_s::impl, and rcl_service_is_valid().
◆ rcl_service_get_service_name()
| RCL_PUBLIC RCL_WARN_UNUSED const char* rcl_service_get_service_name | ( | const rcl_service_t * | service | ) |
Get the topic name for the service.
This function returns the service's internal topic name string. This function can fail, and therefore return NULL, if the:
- service is
NULL - service is invalid (never called init, called fini, or invalid)
The returned string is only valid as long as the service is valid. The value of the string may change if the topic name changes, and therefore copying the string is recommended if this is a concern.
| Attribute | Adherence |
|---|---|
| Allocates Memory | No |
| Thread-Safe | No |
| Uses Atomics | No |
| Lock-Free | Yes |
- Parameters
-
[in] service the pointer to the service
- Returns
- name string if successful, otherwise
NULL
Definition at line 297 of file service.c.
References rcl_service_s::impl, and rcl_service_get_options().
Referenced by rclcpp::ServiceBase::get_service_name().

◆ rcl_service_init()
| RCL_PUBLIC RCL_WARN_UNUSED rcl_ret_t rcl_service_init | ( | rcl_service_t * | service, |
| const rcl_node_t * | node, | ||
| const rosidl_service_type_support_t * | type_support, | ||
| const char * | service_name, | ||
| const rcl_service_options_t * | options | ||
| ) |
Initialize a rcl service.
After calling this function on a rcl_service_t, it can be used to take requests of the given type to the given topic using rcl_take_request(). It can also send a response to a request using rcl_send_response().
The given rcl_node_t must be valid and the resulting rcl_service_t is only valid as long as the given rcl_node_t remains valid.
The rosidl_service_type_support_t is obtained on a per .srv type basis. When the user defines a ROS service, code is generated which provides the required rosidl_service_type_support_t object. This object can be obtained using a language appropriate mechanism.
- Todo:
- TODO(wjwwood) write these instructions once and link to it instead
For C, a macro can be used (for example example_interfaces/AddTwoInts):
For C++, a template function is used:
The rosidl_service_type_support_t object contains service type specific information used to send or take requests and responses.
The topic name must be a c string which follows the topic and service name format rules for unexpanded names, also known as non-fully qualified names:
- See also
- rcl_expand_topic_name
The options struct allows the user to set the quality of service settings as well as a custom allocator which is used when initializing/finalizing the service to allocate space for incidentals, e.g. the service name string.
Expected usage (for C services):
| Attribute | Adherence |
|---|---|
| Allocates Memory | Yes |
| Thread-Safe | No |
| Uses Atomics | No |
| Lock-Free | Yes |
- Parameters
-
[out] service preallocated service structure [in] node valid rcl node handle [in] type_support type support object for the service's type [in] service_name the name of the service [in] options service options, including quality of service settings
- Returns
- RCL_RET_OK if service was initialized successfully, or
- RCL_RET_INVALID_ARGUMENT if any arguments are invalid, or
- RCL_RET_ALREADY_INIT if the service is already initialized, or
- RCL_RET_NODE_INVALID if the node is invalid, or
- RCL_RET_BAD_ALLOC if allocating memory failed, or
- RCL_RET_SERVICE_NAME_INVALID if the given service name is invalid, or
- RCL_RET_ERROR if an unspecified error occurs.
Definition at line 86 of file service.c.
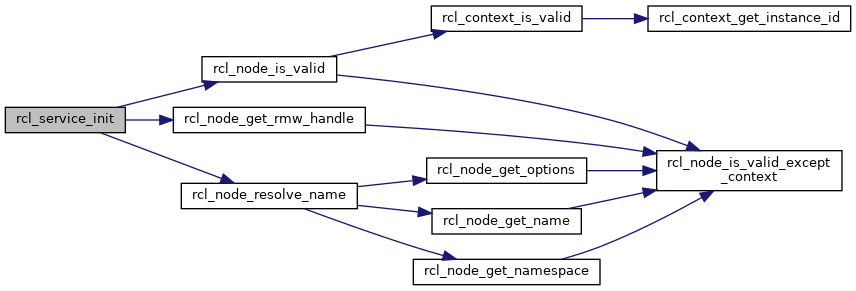
References rcl_service_options_s::allocator, rcl_service_s::impl, rcl_service_options_s::qos, RCL_CHECK_ALLOCATOR_WITH_MSG, rcl_node_get_rmw_handle(), rcl_node_is_valid(), rcl_node_resolve_name(), RCL_RET_ALREADY_INIT, RCL_RET_BAD_ALLOC, RCL_RET_ERROR, RCL_RET_INVALID_ARGUMENT, RCL_RET_NODE_INVALID, RCL_RET_OK, RCL_RET_SERVICE_NAME_INVALID, and RCL_RET_UNKNOWN_SUBSTITUTION.
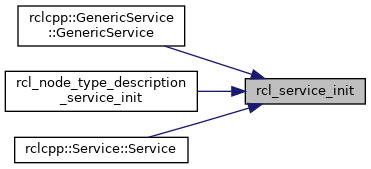
Referenced by rclcpp::GenericService::GenericService(), rcl_node_type_description_service_init(), and rclcpp::Service< ServiceT >::Service().
◆ rcl_service_is_valid()
| RCL_PUBLIC bool rcl_service_is_valid | ( | const rcl_service_t * | service | ) |
Check that the service is valid.
The bool returned is false if service is invalid. The bool returned is true otherwise. In the case where false is to be returned, an error message is set. This function cannot fail.
| Attribute | Adherence |
|---|---|
| Allocates Memory | No |
| Thread-Safe | No |
| Uses Atomics | No |
| Lock-Free | Yes |
- Parameters
-
[in] service pointer to the rcl service
- Returns
trueifserviceis valid, otherwisefalse
Definition at line 425 of file service.c.
References rcl_service_s::impl.
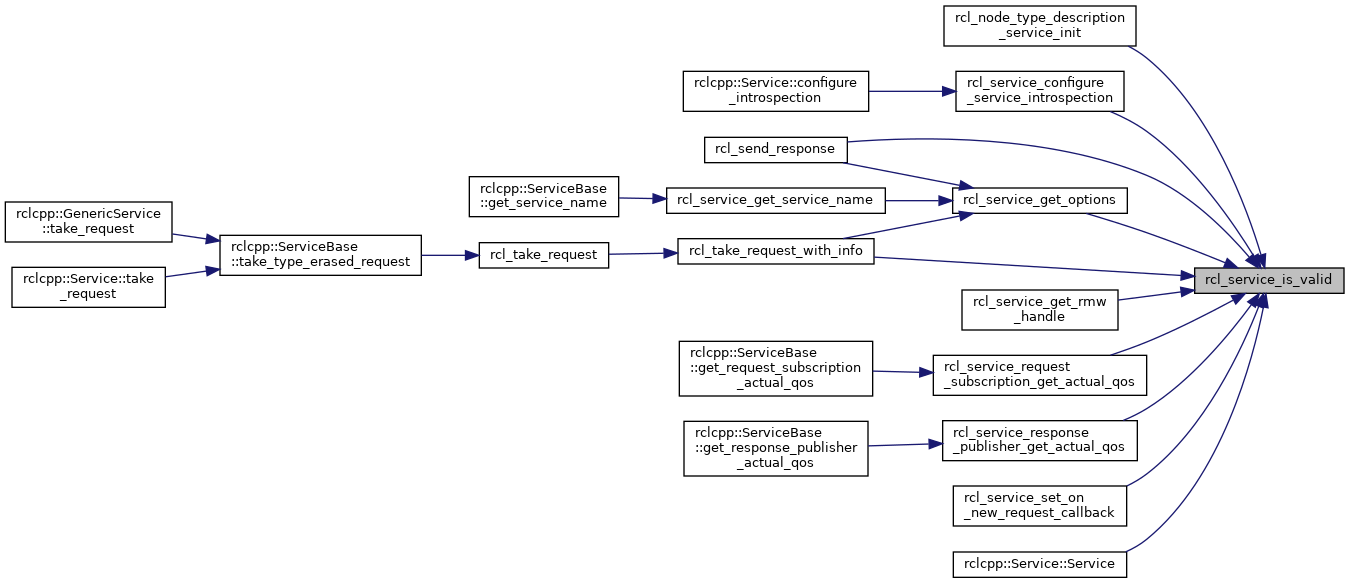
Referenced by rcl_node_type_description_service_init(), rcl_send_response(), rcl_service_configure_service_introspection(), rcl_service_get_options(), rcl_service_get_rmw_handle(), rcl_service_request_subscription_get_actual_qos(), rcl_service_response_publisher_get_actual_qos(), rcl_service_set_on_new_request_callback(), rcl_take_request_with_info(), and rclcpp::Service< ServiceT >::Service().
◆ rcl_service_request_subscription_get_actual_qos()
| RCL_PUBLIC RCL_WARN_UNUSED const rmw_qos_profile_t* rcl_service_request_subscription_get_actual_qos | ( | const rcl_service_t * | service | ) |
Get the actual qos settings of the service's request subscription.
Used to get the actual qos settings of the service's request subscription. The actual configuration applied when using RMW_*_SYSTEM_DEFAULT can only be resolved after the creation of the service, and it depends on the underlying rmw implementation. If the underlying setting in use can't be represented in ROS terms, it will be set to RMW_*_UNKNOWN. The returned struct is only valid as long as the rcl_service_t is valid.
| Attribute | Adherence |
|---|---|
| Allocates Memory | No |
| Thread-Safe | Yes |
| Uses Atomics | No |
| Lock-Free | Yes |
- Parameters
-
[in] service pointer to the rcl service
- Returns
- qos struct if successful, otherwise
NULL
Definition at line 436 of file service.c.
References rcl_service_s::impl, and rcl_service_is_valid().
Referenced by rclcpp::ServiceBase::get_request_subscription_actual_qos().
◆ rcl_service_response_publisher_get_actual_qos()
| RCL_PUBLIC RCL_WARN_UNUSED const rmw_qos_profile_t* rcl_service_response_publisher_get_actual_qos | ( | const rcl_service_t * | service | ) |
Get the actual qos settings of the service's response publisher.
Used to get the actual qos settings of the service's response publisher. The actual configuration applied when using RMW_*_SYSTEM_DEFAULT can only be resolved after the creation of the service, and it depends on the underlying rmw implementation. If the underlying setting in use can't be represented in ROS terms, it will be set to RMW_*_UNKNOWN. The returned struct is only valid as long as the rcl_service_t is valid.
| Attribute | Adherence |
|---|---|
| Allocates Memory | No |
| Thread-Safe | Yes |
| Uses Atomics | No |
| Lock-Free | Yes |
- Parameters
-
[in] service pointer to the rcl service
- Returns
- qos struct if successful, otherwise
NULL
Definition at line 445 of file service.c.
References rcl_service_s::impl, and rcl_service_is_valid().
Referenced by rclcpp::ServiceBase::get_response_publisher_actual_qos().
◆ rcl_service_set_on_new_request_callback()
| RCL_PUBLIC RCL_WARN_UNUSED rcl_ret_t rcl_service_set_on_new_request_callback | ( | const rcl_service_t * | service, |
| rcl_event_callback_t | callback, | ||
| const void * | user_data | ||
| ) |
Set the on new request callback function for the service.
This API sets the callback function to be called whenever the service is notified about a new request.
- See also
- rmw_service_set_on_new_request_callback for details about this function.
| Attribute | Adherence |
|---|---|
| Allocates Memory | No |
| Thread-Safe | Yes |
| Uses Atomics | Maybe [1] |
| Lock-Free | Maybe [1] |
[1] rmw implementation defined
- Parameters
-
[in] service The service on which to set the callback [in] callback The callback to be called when new requests arrive, may be NULL [in] user_data Given to the callback when called later, may be NULL
- Returns
RCL_RET_OKif callback was set to the listener, or-
RCL_RET_INVALID_ARGUMENTifserviceis NULL, or -
RCL_RET_UNSUPPORTEDif the API is not supported by the middleware
Definition at line 454 of file service.c.
References rcl_service_s::impl, RCL_RET_INVALID_ARGUMENT, and rcl_service_is_valid().
◆ rcl_take_request()
| RCL_PUBLIC RCL_WARN_UNUSED rcl_ret_t rcl_take_request | ( | const rcl_service_t * | service, |
| rmw_request_id_t * | request_header, | ||
| void * | ros_request | ||
| ) |
Backwards compatibility function to take a pending ROS request using a rcl service.
This version takes a request ID only. See rcl_take_request_with_info() for a full explanation of what this does.
- Parameters
-
[in] service the handle to the service from which to take [in,out] request_header ptr to the struct holding the id of the request [in,out] ros_request type-erased ptr to an allocated ROS request message
- Returns
- RCL_RET_OK if the request was taken, or
- RCL_RET_INVALID_ARGUMENT if any arguments are invalid, or
- RCL_RET_SERVICE_INVALID if the service is invalid, or
- RCL_RET_BAD_ALLOC if allocating memory failed, or
- RCL_RET_SERVICE_TAKE_FAILED if take failed but no error occurred in the middleware, or
- RCL_RET_ERROR if an unspecified error occurs.
Definition at line 371 of file service.c.
References rcl_take_request_with_info().
Referenced by rclcpp::ServiceBase::take_type_erased_request().


◆ rcl_take_request_with_info()
| RCL_PUBLIC RCL_WARN_UNUSED rcl_ret_t rcl_take_request_with_info | ( | const rcl_service_t * | service, |
| rmw_service_info_t * | request_header, | ||
| void * | ros_request | ||
| ) |
Take a pending ROS request using a rcl service.
It is the job of the caller to ensure that the type of the ros_request argument and the type associate with the service, via the type support, match. Passing a different type to rcl_take produces undefined behavior and cannot be checked by this function and therefore no deliberate error will occur.
TODO(jacquelinekay) blocking of take? TODO(jacquelinekay) pre-, during-, and post-conditions for message ownership? TODO(jacquelinekay) is rcl_take_request thread-safe? TODO(jacquelinekay) Should there be an rcl_request_id_t?
The ros_request pointer should point to an already allocated ROS request message struct of the correct type, into which the taken ROS request will be copied if one is available. If taken is false after calling, then the ROS request will be unmodified.
If allocation is required when taking the request, e.g. if space needs to be allocated for a dynamically sized array in the target message, then the allocator given in the service options is used.
request_header is a pointer to pre-allocated a rmw struct containing meta-information about the request (e.g. the sequence number).
| Attribute | Adherence |
|---|---|
| Allocates Memory | Maybe [1] |
| Thread-Safe | No |
| Uses Atomics | No |
| Lock-Free | Yes |
[1] only if required when filling the request, avoided for fixed sizes
- Parameters
-
[in] service the handle to the service from which to take [in,out] request_header ptr to the struct holding metadata about the request [in,out] ros_request type-erased ptr to an allocated ROS request message
- Returns
- RCL_RET_OK if the request was taken, or
- RCL_RET_INVALID_ARGUMENT if any arguments are invalid, or
- RCL_RET_SERVICE_INVALID if the service is invalid, or
- RCL_RET_BAD_ALLOC if allocating memory failed, or
- RCL_RET_SERVICE_TAKE_FAILED if take failed but no error occurred in the middleware, or
- RCL_RET_ERROR if an unspecified error occurs.
Definition at line 326 of file service.c.
References rcl_service_s::impl, RCL_RET_BAD_ALLOC, RCL_RET_ERROR, RCL_RET_INVALID_ARGUMENT, RCL_RET_OK, RCL_RET_SERVICE_INVALID, RCL_RET_SERVICE_TAKE_FAILED, rcl_service_get_options(), and rcl_service_is_valid().
Referenced by rcl_take_request().