Public Member Functions | |
| RCLCPP_PUBLIC | ClientBase (rclcpp::node_interfaces::NodeBaseInterface *node_base, rclcpp::node_interfaces::NodeGraphInterface::SharedPtr node_graph) |
| RCLCPP_PUBLIC bool | take_type_erased_response (void *response_out, rmw_request_id_t &request_header_out) |
| Take the next response for this client as a type erased pointer. More... | |
| RCLCPP_PUBLIC const char * | get_service_name () const |
| Return the name of the service. More... | |
| RCLCPP_PUBLIC std::shared_ptr< rcl_client_t > | get_client_handle () |
| Return the rcl_client_t client handle in a std::shared_ptr. More... | |
| RCLCPP_PUBLIC std::shared_ptr< const rcl_client_t > | get_client_handle () const |
| Return the rcl_client_t client handle in a std::shared_ptr. More... | |
| RCLCPP_PUBLIC bool | service_is_ready () const |
| Return if the service is ready. More... | |
| template<typename RepT = int64_t, typename RatioT = std::milli> | |
| bool | wait_for_service (std::chrono::duration< RepT, RatioT > timeout=std::chrono::duration< RepT, RatioT >(-1)) |
| Wait for a service to be ready. More... | |
| virtual std::shared_ptr< void > | create_response ()=0 |
| virtual std::shared_ptr< rmw_request_id_t > | create_request_header ()=0 |
| virtual void | handle_response (std::shared_ptr< rmw_request_id_t > request_header, std::shared_ptr< void > response)=0 |
| RCLCPP_PUBLIC bool | exchange_in_use_by_wait_set_state (bool in_use_state) |
| Exchange the "in use by wait set" state for this client. More... | |
| RCLCPP_PUBLIC rclcpp::QoS | get_request_publisher_actual_qos () const |
| Get the actual request publsher QoS settings, after the defaults have been determined. More... | |
| RCLCPP_PUBLIC rclcpp::QoS | get_response_subscription_actual_qos () const |
| Get the actual response subscription QoS settings, after the defaults have been determined. More... | |
| void | set_on_new_response_callback (std::function< void(size_t)> callback) |
| Set a callback to be called when each new response is received. More... | |
| void | clear_on_new_response_callback () |
| Unset the callback registered for new responses, if any. | |
Protected Member Functions | |
| RCLCPP_PUBLIC bool | wait_for_service_nanoseconds (std::chrono::nanoseconds timeout) |
| RCLCPP_PUBLIC rcl_node_t * | get_rcl_node_handle () |
| RCLCPP_PUBLIC const rcl_node_t * | get_rcl_node_handle () const |
| RCLCPP_PUBLIC void | set_on_new_response_callback (rcl_event_callback_t callback, const void *user_data) |
Protected Attributes | |
| rclcpp::node_interfaces::NodeGraphInterface::WeakPtr | node_graph_ |
| std::shared_ptr< rcl_node_t > | node_handle_ |
| std::shared_ptr< rclcpp::Context > | context_ |
| rclcpp::Logger | node_logger_ |
| std::recursive_mutex | callback_mutex_ |
| std::function< void(size_t)> | on_new_response_callback_ {nullptr} |
| std::shared_ptr< rcl_client_t > | client_handle_ |
| std::atomic< bool > | in_use_by_wait_set_ {false} |
Detailed Description
Definition at line 140 of file client.hpp.
Member Function Documentation
◆ exchange_in_use_by_wait_set_state()
| bool ClientBase::exchange_in_use_by_wait_set_state | ( | bool | in_use_state | ) |
Exchange the "in use by wait set" state for this client.
This is used to ensure this client is not used by multiple wait sets at the same time.
- Parameters
-
[in] in_use_state the new state to exchange into the state, true indicates it is now in use by a wait set, and false is that it is no longer in use by a wait set.
- Returns
- the previous state.
Definition at line 194 of file client.cpp.
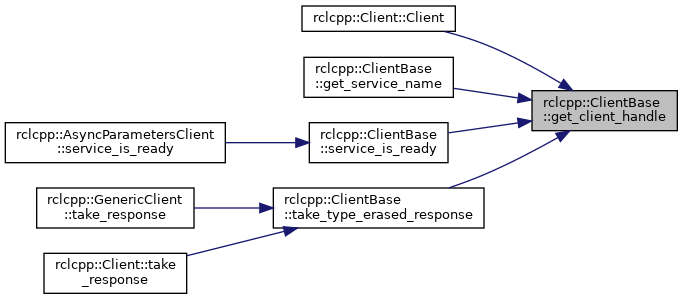
◆ get_client_handle() [1/2]
| std::shared_ptr< rcl_client_t > ClientBase::get_client_handle | ( | ) |
Return the rcl_client_t client handle in a std::shared_ptr.
This handle remains valid after the Client is destroyed. The actual rcl client is not finalized until it is out of scope everywhere.
Definition at line 92 of file client.cpp.
Referenced by rclcpp::Client< ServiceT >::Client(), get_service_name(), service_is_ready(), and take_type_erased_response().
◆ get_client_handle() [2/2]
| std::shared_ptr< const rcl_client_t > ClientBase::get_client_handle | ( | ) | const |
Return the rcl_client_t client handle in a std::shared_ptr.
This handle remains valid after the Client is destroyed. The actual rcl client is not finalized until it is out of scope everywhere.
Definition at line 98 of file client.cpp.
◆ get_request_publisher_actual_qos()
| rclcpp::QoS ClientBase::get_request_publisher_actual_qos | ( | ) | const |
Get the actual request publsher QoS settings, after the defaults have been determined.
The actual configuration applied when using RMW_QOS_POLICY_*_SYSTEM_DEFAULT can only be resolved after the creation of the client, and it depends on the underlying rmw implementation. If the underlying setting in use can't be represented in ROS terms, it will be set to RMW_QOS_POLICY_*_UNKNOWN. May throw runtime_error when an unexpected error occurs.
- Returns
- The actual request publsher qos settings.
- Exceptions
-
std::runtime_error if failed to get qos settings
Definition at line 200 of file client.cpp.
References rclcpp::QoSInitialization::from_rmw(), and rcl_client_request_publisher_get_actual_qos().

◆ get_response_subscription_actual_qos()
| rclcpp::QoS ClientBase::get_response_subscription_actual_qos | ( | ) | const |
Get the actual response subscription QoS settings, after the defaults have been determined.
The actual configuration applied when using RMW_QOS_POLICY_*_SYSTEM_DEFAULT can only be resolved after the creation of the client, and it depends on the underlying rmw implementation. If the underlying setting in use can't be represented in ROS terms, it will be set to RMW_QOS_POLICY_*_UNKNOWN. May throw runtime_error when an unexpected error occurs.
- Returns
- The actual response subscription qos settings.
- Exceptions
-
std::runtime_error if failed to get qos settings
Definition at line 219 of file client.cpp.
References rclcpp::QoSInitialization::from_rmw(), and rcl_client_response_subscription_get_actual_qos().

◆ get_service_name()
| const char * ClientBase::get_service_name | ( | ) | const |
Return the name of the service.
- Returns
- The name of the service.
Definition at line 86 of file client.cpp.
References get_client_handle(), and rcl_client_get_service_name().

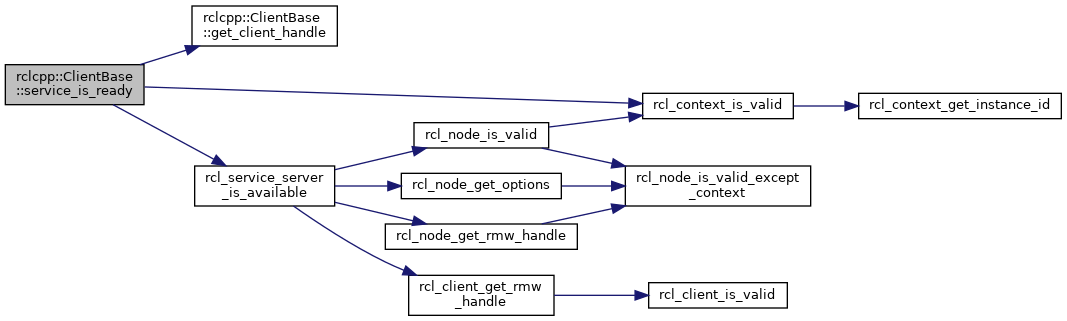
◆ service_is_ready()
| bool ClientBase::service_is_ready | ( | ) | const |
Return if the service is ready.
- Returns
trueif the service is ready,falseotherwise
Definition at line 104 of file client.cpp.
References rcl_node_s::context, get_client_handle(), rcl_context_is_valid(), RCL_RET_NODE_INVALID, RCL_RET_OK, and rcl_service_server_is_available().
Referenced by rclcpp::AsyncParametersClient::service_is_ready().
◆ set_on_new_response_callback()
|
inline |
Set a callback to be called when each new response is received.
The callback receives a size_t which is the number of responses received since the last time this callback was called. Normally this is 1, but can be > 1 if responses were received before any callback was set.
Since this callback is called from the middleware, you should aim to make it fast and not blocking. If you need to do a lot of work or wait for some other event, you should spin it off to another thread, otherwise you risk blocking the middleware.
Calling it again will clear any previously set callback.
An exception will be thrown if the callback is not callable.
This function is thread-safe.
If you want more information available in the callback, like the client or other information, you may use a lambda with captures or std::bind.
- See also
- rmw_client_set_on_new_response_callback
- rcl_client_set_on_new_response_callback
- Parameters
-
[in] callback functor to be called when a new response is received
Definition at line 299 of file client.hpp.
Referenced by clear_on_new_response_callback().
◆ take_type_erased_response()
| bool ClientBase::take_type_erased_response | ( | void * | response_out, |
| rmw_request_id_t & | request_header_out | ||
| ) |
Take the next response for this client as a type erased pointer.
The type erased pointer allows for this method to be used in a type agnostic way along with ClientBase::create_response(), ClientBase::create_request_header(), and ClientBase::handle_response(). The typed version of this can be used if the Service type is known,
- See also
- Client::take_response().
- Parameters
-
[out] response_out The type erased pointer to a Service Response into which the middleware will copy the response being taken. [out] request_header_out The request header to be filled by the middleware when taking, and which can be used to associte the response to a specific request.
- Returns
- true if the response was taken, otherwise false.
- Exceptions
-
rclcpp::exceptions::RCLError based exceptions if the underlying rcl function fail.
Definition at line 71 of file client.cpp.
References get_client_handle(), RCL_RET_CLIENT_TAKE_FAILED, RCL_RET_OK, and rcl_take_response().
Referenced by rclcpp::GenericClient::take_response(), and rclcpp::Client< ServiceT >::take_response().
◆ wait_for_service()
|
inline |
Wait for a service to be ready.
- Parameters
-
timeout maximum time to wait
- Returns
trueif the service is ready and the timeout is not over,falseotherwise
Definition at line 213 of file client.hpp.
The documentation for this class was generated from the following files:
- rclcpp/include/rclcpp/client.hpp
- rclcpp/src/rclcpp/client.cpp