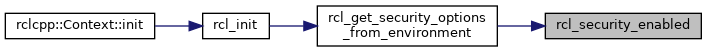#include <stdbool.h>#include "rcl/allocator.h"#include "rcl/types.h"#include "rcl/visibility_control.h"#include "rmw/security_options.h"
Go to the source code of this file.
Macros | |
| #define | ROS_SECURITY_ENCLAVE_OVERRIDE "ROS_SECURITY_ENCLAVE_OVERRIDE" |
| The name of the environment variable containing the security enclave override. | |
| #define | ROS_SECURITY_KEYSTORE_VAR_NAME "ROS_SECURITY_KEYSTORE" |
| The name of the environment variable containing the path to the keystore. | |
| #define | ROS_SECURITY_STRATEGY_VAR_NAME "ROS_SECURITY_STRATEGY" |
| The name of the environment variable containing the security strategy. | |
| #define | ROS_SECURITY_ENABLE_VAR_NAME "ROS_SECURITY_ENABLE" |
| The name of the environment variable controlling whether security is enabled. | |
Functions | |
| RCL_PUBLIC rcl_ret_t | rcl_get_security_options_from_environment (const char *name, const rcutils_allocator_t *allocator, rmw_security_options_t *security_options) |
| Initialize security options from values in the environment variables and given names. More... | |
| RCL_PUBLIC rcl_ret_t | rcl_security_enabled (bool *use_security) |
| Check if security has to be used, according to the environment. More... | |
| RCL_PUBLIC rcl_ret_t | rcl_get_enforcement_policy (rmw_security_enforcement_policy_t *policy) |
| Get security enforcement policy from the environment. More... | |
| RCL_PUBLIC char * | rcl_get_secure_root (const char *name, const rcl_allocator_t *allocator) |
| Return the secure root given a enclave name. More... | |
Function Documentation
◆ rcl_get_enforcement_policy()
| RCL_PUBLIC rcl_ret_t rcl_get_enforcement_policy | ( | rmw_security_enforcement_policy_t * | policy | ) |
Get security enforcement policy from the environment.
Sets policy based on the value of the ROS_SECURITY_STRATEGY environment variable. If ROS_SECURITY_STRATEGY is "Enforce", policy will be RMW_SECURITY_ENFORCEMENT_ENFORCE. If not, policy will be RMW_SECURITY_ENFORCEMENT_PERMISSIVE.
- Parameters
-
[out] policy Must not be NULL.
- Returns
- RCL_RET_INVALID_ARGUMENT if an argument is not valid, or
- RCL_RET_ERROR if an unexpected error happened, or
- RCL_RET_OK.
Definition at line 87 of file security.c.
References RCL_RET_ERROR, RCL_RET_INVALID_ARGUMENT, RCL_RET_OK, and ROS_SECURITY_STRATEGY_VAR_NAME.
Referenced by rcl_get_security_options_from_environment().
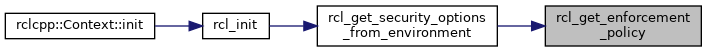
◆ rcl_get_secure_root()
| RCL_PUBLIC char* rcl_get_secure_root | ( | const char * | name, |
| const rcl_allocator_t * | allocator | ||
| ) |
Return the secure root given a enclave name.
Return the security directory associated with the enclave name.
The value of the environment variable ROS_SECURITY_KEYSTORE is used as a root. The specific directory to be used is found from that root using the name passed. E.g. for a context named "/a/b/c" and root "/r", the secure root path will be "/r/a/b/c", where the delimiter "/" is native for target file system (e.g. "\\" for _WIN32).
However, this expansion can be overridden by setting the secure enclave override environment (ROS_SECURITY_ENCLAVE_OVERRIDE) variable, allowing users to explicitly specify the exact enclave name to be utilized. Such an override is useful for applications where the enclave is non-deterministic before runtime, or when testing and using additional tools that may not otherwise be easily provisioned.
- Parameters
-
[in] name validated name (a single token) [in] allocator the allocator to use for allocation
- Returns
- Machine specific (absolute) enclave directory path or NULL on failure. Returned pointer must be deallocated by the caller of this function
Definition at line 149 of file security.c.
References RCL_CHECK_ALLOCATOR_WITH_MSG, ROS_SECURITY_ENCLAVE_OVERRIDE, and ROS_SECURITY_KEYSTORE_VAR_NAME.
Referenced by rcl_get_security_options_from_environment().
◆ rcl_get_security_options_from_environment()
| RCL_PUBLIC rcl_ret_t rcl_get_security_options_from_environment | ( | const char * | name, |
| const rcutils_allocator_t * | allocator, | ||
| rmw_security_options_t * | security_options | ||
| ) |
Initialize security options from values in the environment variables and given names.
Initialize the given security options based on the environment. For more details:
- Parameters
-
[in] name name used to find the security root path. [in] allocator used to do allocations. [out] security_options security options that will be configured according to the environment.
- Returns
- RCL_RET_OK If the security options are returned properly, or
- RCL_RET_INVALID_ARGUMENT if an argument is not valid, or
- RCL_RET_ERROR if an unexpected error happened
Definition at line 29 of file security.c.
References rcl_get_enforcement_policy(), rcl_get_secure_root(), RCL_RET_ERROR, RCL_RET_OK, and rcl_security_enabled().
Referenced by rcl_init().
◆ rcl_security_enabled()
| RCL_PUBLIC rcl_ret_t rcl_security_enabled | ( | bool * | use_security | ) |
Check if security has to be used, according to the environment.
If the ROS_SECURITY_ENABLE environment variable is set to "true", use_security will be set to true.
- Parameters
-
[out] use_security Must not be NULL.
- Returns
- RCL_RET_INVALID_ARGUMENT if an argument is not valid, or
- RCL_RET_ERROR if an unexpected error happened, or
- RCL_RET_OK.
Definition at line 67 of file security.c.
References RCL_RET_ERROR, RCL_RET_INVALID_ARGUMENT, RCL_RET_OK, and ROS_SECURITY_ENABLE_VAR_NAME.
Referenced by rcl_get_security_options_from_environment().