Public Member Functions | |
| RCLCPP_PUBLIC | TimerBase (Clock::SharedPtr clock, std::chrono::nanoseconds period, rclcpp::Context::SharedPtr context, bool autostart=true) |
| TimerBase constructor. More... | |
| virtual RCLCPP_PUBLIC | ~TimerBase () |
| TimerBase destructor. | |
| RCLCPP_PUBLIC void | cancel () |
| Cancel the timer. More... | |
| RCLCPP_PUBLIC bool | is_canceled () |
| Return the timer cancellation state. More... | |
| RCLCPP_PUBLIC void | reset () |
| Reset the timer. More... | |
| virtual RCLCPP_PUBLIC std::shared_ptr< void > | call ()=0 |
| Indicate that we're about to execute the callback. More... | |
| virtual RCLCPP_PUBLIC void | execute_callback (const std::shared_ptr< void > &data)=0 |
| Call the callback function when the timer signal is emitted. More... | |
| RCLCPP_PUBLIC std::shared_ptr< const rcl_timer_t > | get_timer_handle () |
| RCLCPP_PUBLIC std::chrono::nanoseconds | time_until_trigger () |
| Check how long the timer has until its next scheduled callback. More... | |
| virtual bool | is_steady ()=0 |
| Is the clock steady (i.e. is the time between ticks constant?) More... | |
| RCLCPP_PUBLIC bool | is_ready () |
| Check if the timer is ready to trigger the callback. More... | |
| RCLCPP_PUBLIC bool | exchange_in_use_by_wait_set_state (bool in_use_state) |
| Exchange the "in use by wait set" state for this timer. More... | |
| RCLCPP_PUBLIC void | set_on_reset_callback (std::function< void(size_t)> callback) |
| Set a callback to be called when the timer is reset. More... | |
| RCLCPP_PUBLIC void | clear_on_reset_callback () |
| Unset the callback registered for reset timer. | |
Protected Member Functions | |
| RCLCPP_PUBLIC void | set_on_reset_callback (rcl_event_callback_t callback, const void *user_data) |
Protected Attributes | |
| std::recursive_mutex | callback_mutex_ |
| std::function< void(size_t)> | on_reset_callback_ {nullptr} |
| Clock::SharedPtr | clock_ |
| std::shared_ptr< rcl_timer_t > | timer_handle_ |
| std::atomic< bool > | in_use_by_wait_set_ {false} |
Detailed Description
Constructor & Destructor Documentation
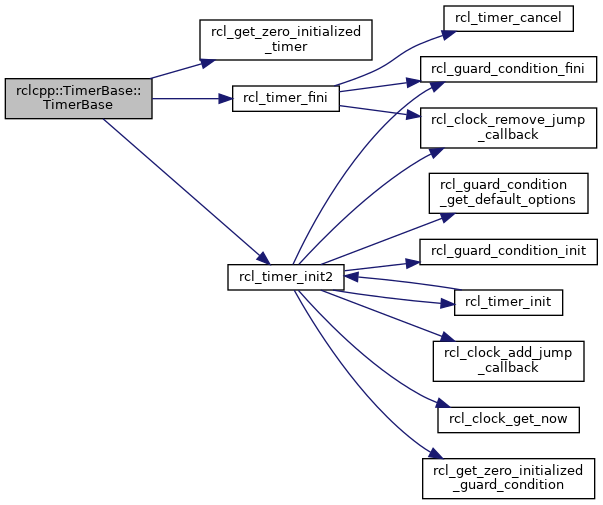
◆ TimerBase()
|
explicit |
TimerBase constructor.
- Parameters
-
clock A clock to use for time and sleeping period The interval at which the timer fires context node context autostart timer state on initialization
In order to activate a timer that is not started on initialization, user should call the reset() method.
Definition at line 32 of file timer.cpp.
References rcl_get_default_allocator, rcl_get_zero_initialized_timer(), RCL_RET_OK, rcl_timer_fini(), and rcl_timer_init2().
Member Function Documentation
◆ call()
|
pure virtual |
Indicate that we're about to execute the callback.
The multithreaded executor takes advantage of this to avoid scheduling the callback multiple times.
- Returns
- a valid shared_ptr if the callback should be executed, an invalid shared_ptr (nullptr) if the timer was canceled.
Implemented in rclcpp::GenericTimer< FunctorT, >.
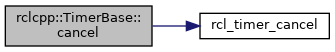
◆ cancel()
| void TimerBase::cancel | ( | ) |
Cancel the timer.
- Exceptions
-
std::runtime_error if the rcl_timer_cancel returns a failure
Definition at line 83 of file timer.cpp.
References RCL_RET_OK, and rcl_timer_cancel().
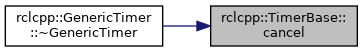
Referenced by rclcpp::GenericTimer< FunctorT, >::~GenericTimer().
◆ exchange_in_use_by_wait_set_state()
| bool TimerBase::exchange_in_use_by_wait_set_state | ( | bool | in_use_state | ) |
Exchange the "in use by wait set" state for this timer.
This is used to ensure this timer is not used by multiple wait sets at the same time.
- Parameters
-
[in] in_use_state the new state to exchange into the state, true indicates it is now in use by a wait set, and false is that it is no longer in use by a wait set.
- Returns
- the previous state.
◆ execute_callback()
|
pure virtual |
Call the callback function when the timer signal is emitted.
- Parameters
-
[in] data the pointer returned by the call function
Implemented in rclcpp::GenericTimer< FunctorT, >.
◆ is_canceled()
| bool TimerBase::is_canceled | ( | ) |
Return the timer cancellation state.
- Returns
- true if the timer has been cancelled, false otherwise
- Exceptions
-
std::runtime_error if the rcl_get_error_state returns 0 rclcpp::exceptions::RCLError some child class exception based on ret
Definition at line 92 of file timer.cpp.
References RCL_RET_OK, and rcl_timer_is_canceled().
◆ is_ready()
| bool TimerBase::is_ready | ( | ) |
Check if the timer is ready to trigger the callback.
This function expects its caller to immediately trigger the callback after this function, since it maintains the last time the callback was triggered.
- Returns
- True if the timer needs to trigger.
- Exceptions
-
std::runtime_error if it failed to check timer
Definition at line 116 of file timer.cpp.
References RCL_RET_OK, and rcl_timer_is_ready().

◆ is_steady()
|
pure virtual |
Is the clock steady (i.e. is the time between ticks constant?)
- Returns
- True if the clock used by this timer is steady.
Implemented in rclcpp::GenericTimer< FunctorT, >.
◆ reset()
| void TimerBase::reset | ( | ) |
Reset the timer.
- Exceptions
-
std::runtime_error if the rcl_timer_reset returns a failure
Definition at line 103 of file timer.cpp.
References RCL_RET_OK, and rcl_timer_reset().
◆ set_on_reset_callback()
| void TimerBase::set_on_reset_callback | ( | std::function< void(size_t)> | callback | ) |
Set a callback to be called when the timer is reset.
You should aim to make this callback fast and not blocking. If you need to do a lot of work or wait for some other event, you should spin it off to another thread.
Calling it again will override any previously set callback. An exception will be thrown if the callback is not callable.
This function is thread-safe.
If you want more information available in the callback, you may use a lambda with captures or std::bind.
- Parameters
-
[in] callback functor to be called whenever timer is reset
Definition at line 153 of file timer.cpp.
References rclcpp::get_logger(), and set_on_reset_callback().
Referenced by clear_on_reset_callback(), and set_on_reset_callback().
◆ time_until_trigger()
| std::chrono::nanoseconds TimerBase::time_until_trigger | ( | ) |
Check how long the timer has until its next scheduled callback.
- Returns
- A std::chrono::duration representing the relative time until the next callback or std::chrono::nanoseconds::max() if the timer is canceled.
- Exceptions
-
std::runtime_error if the rcl_timer_get_time_until_next_call returns a failure
Definition at line 127 of file timer.cpp.
References RCL_RET_OK, RCL_RET_TIMER_CANCELED, and rcl_timer_get_time_until_next_call().

The documentation for this class was generated from the following files: